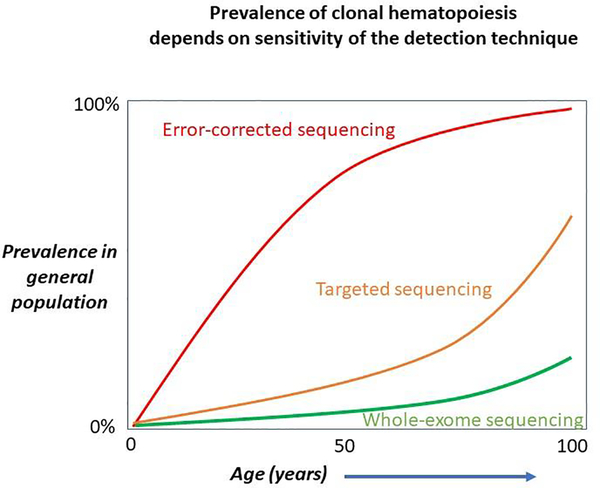
Figure 2:
The prevalence of clonal hematopoiesis depends on the analytical sensitivity of the technique used to detect it. With very sensitive techniques, such as error-corrected methods that can detect populations with a variant allele frequency (VAF) of <0.01%, clonal hematopoiesis is almost universally observed by middle age. Whole-exome and whole-genome sequencing techniques typically have less depth of coverage and sensitivity, and may not detect clonal hematopoiesis below 7–10% VAF. Targeted sequencing platforms with >100x depth of coverage may be able to detect clonal hematopoiesis at the 1–2% VAF level and in this setting the prevalence of clonal hematopoiesis exceeds 10% by age 65–70 years Adapted from reference 1, with permission.