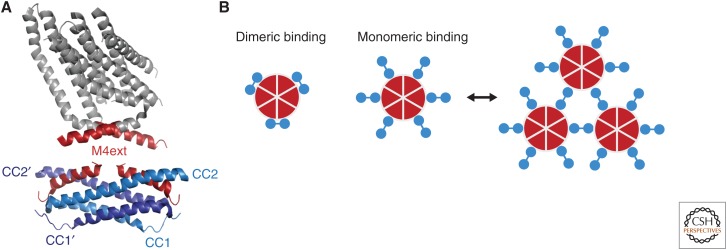
Figure 4.
Dimeric and monomeric models of STIM1-Orai1 binding. (A) A dimeric binding model, showing two subunits from the crystal structure of dOrai (top), with the cytoplasmic M4ext regions highlighted in red (4HKR.pdb) (Hou et al. 2012). The nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy structure below shows two corresponding human Orai1 M4ext fragments (aa 272–292) bound to a dimer of CC1–CC2 STIM1 fragments (aa 312–383; 2MAK.pdb) (Stathopulos et al. 2013). (B) Schematic views of dimeric and monomeric binding models in which three or six STIM1 dimers (blue) are bound to the six Orai1 subunits (red), respectively. Monomeric binding may allow STIM1 dimers to create cross-linked arrays of channels (right).