Figure 3.
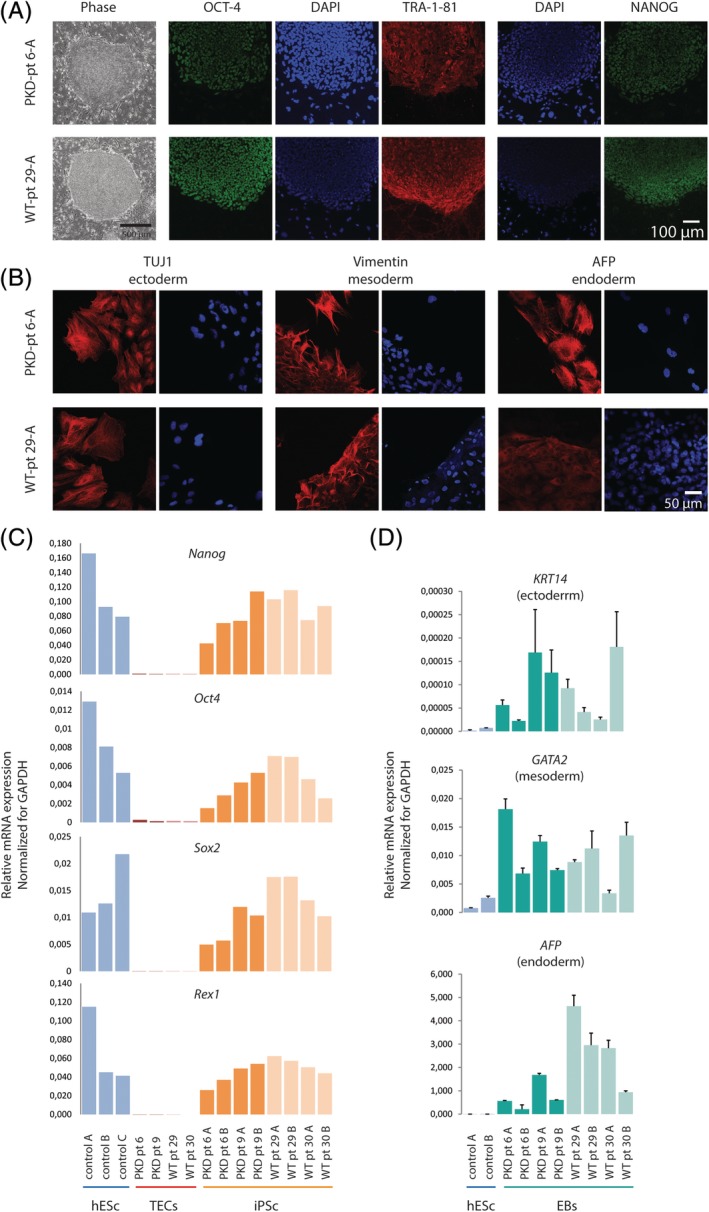
Establishment and characterization of polycystic kidney disease (PKD) patient and normal renal epithelial derived induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). A, Bright field picture of morphology of representative PKD and wild‐type iPSC colonies. Shown are immunocytochemistry stainings for stem cell markers: OCT4, TRA‐1‐81, NANOG (scale bar = 100 μm for all panels). B, Random differentiation if iPSCs to embryoid bodies. Immunocytochemistry stainings for markers of all three germ layers: ectoderm (TUJ), mesoderm (Vimentin), endoderm (AFP) (scale bar = 50 μm for all panels). C, qRT‐PCR, detecting expression of endogenous pluripotency genes; NANOG, OCT4, SOX2, and REX1, iPSC lines and the parental tubular epithelial cell lines and positive control human embryonic stem cells (hESCs). D, Random differentiation of iPSCs to embryoid bodies. Expression of genes specific for each of the three germ layers is shown by qRT‐PCR; hESCs were used as negative control
