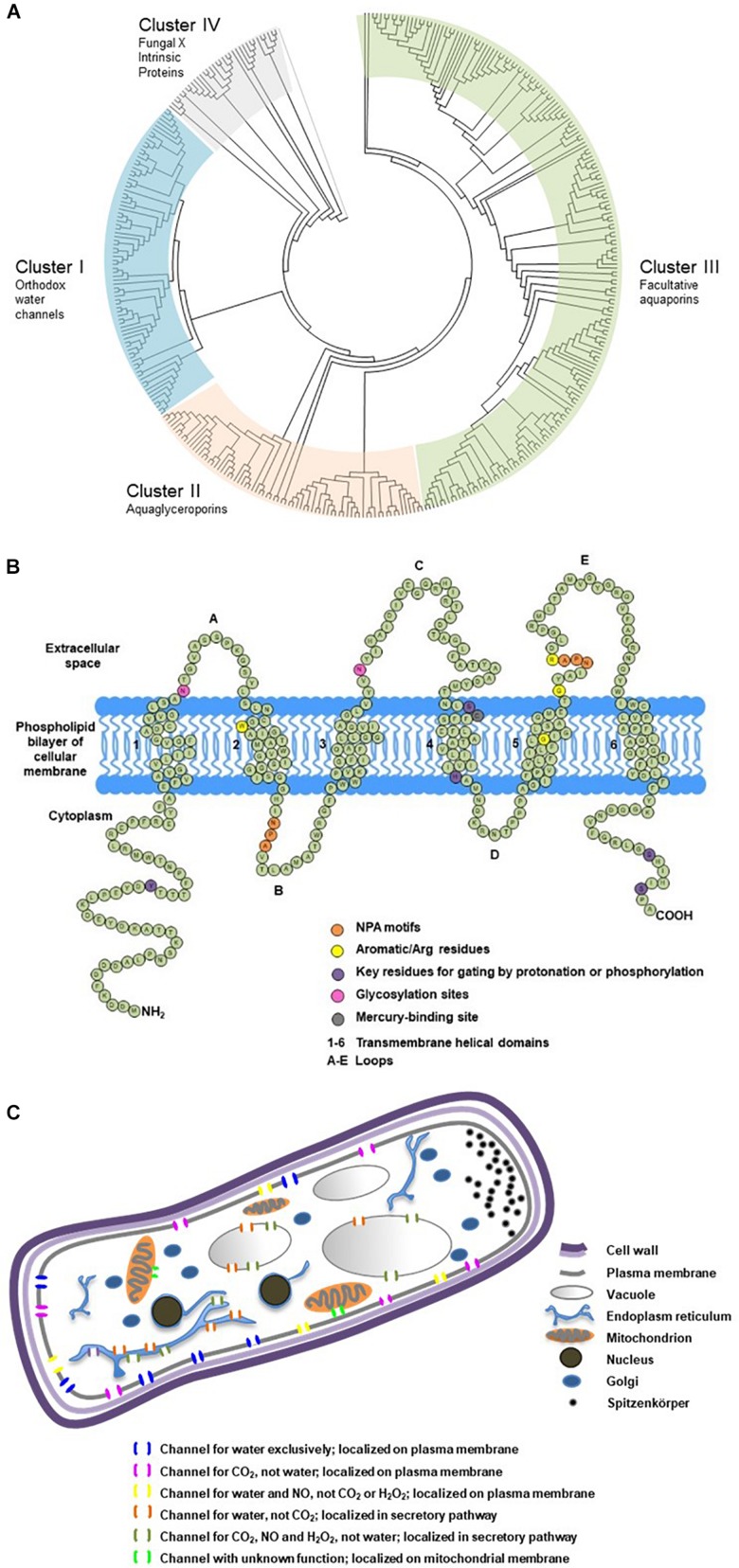
FIGURE 2.
Phylogenetic classification, secondary structure and cellular localization of ectomycorrhizal fungal aquaporins. (A) Phylogenetic analysis of 376 fungal major intrinsic proteins (MIPs), including 152 sequences from 32 EcM fungi categorized into four clusters. The sequences were retrieved from public databases in JGI and NCBI. The classification referred to Xu et al. (2013). Divergence times for all branching points in the topology were calculated using the Maximum Likelihood method based on the JTT matrix-based model (Jones et al., 1992; Tamura et al., 2012) in MEGA 7 (Kumar et al., 2016). The tree was outgrouped to the aquaporin sequences of AqpZ from Escherichia coli and AQP1 from Mus musculus. (B) Transmembrane domains and signature motifs of fungal aquaporins. Protein secondary structure was predicted using SOSUI (Hirokawa et al., 1998). The diagram was reproduced from Xu (2015) with the author’s permission. (C) Possible subcellular localizations and transport functions of fungal aquaporins. Subcellular localization was predicted using TargetP (Emanuelsson et al., 2007). The diagram was modified from Xu (2015) with the author’s permission.