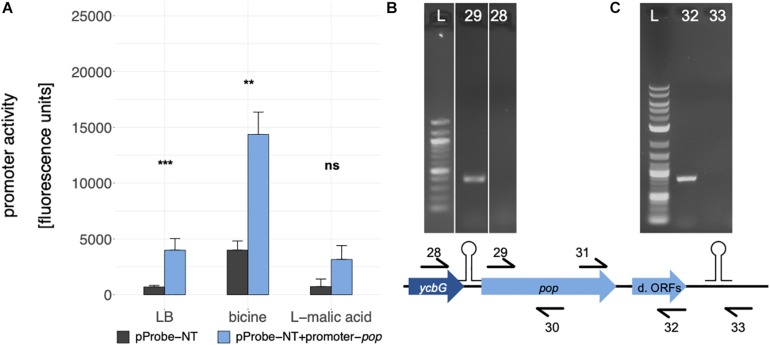
FIGURE 5.
Analysis of the pop transcriptional unit. (A) Promoter activity assay for the promoter of pop, which was introduced in the promoterless GFP vector pProbe-NT. Mean fluorescence units of E. coli Top10 cells with the different constructs in culture conditions as indicated are given. Error bars show standard deviations. Statistical significance between empty vector (gray bars) and the promoter construct (blue bars) was tested with a Welch two sample t-test (** p ≤ 0.01; *** p ≤ 0.001; ns, not significant). (B) Test for mono- or polycistronic mRNA. An agarose gel of RT-PCRs is shown. RNA was reverse transcribed in cDNA with pop specific reverse primer 30. Two different forward primers, binding within ycbG (no. 28) or within pop (no. 29), were combined with a pop reverse primer (no. 30). L: 100 bp DNA Ladder (NEB); 28: PCR with primers 28 + 30; 29: PCR with primers 29 + 30. (C) Test for the predicted rho-independent terminator. An agarose gel of RT-PCRs is shown. RNA was reverse transcribed in cDNA with pop specific reverse primers 32 or 33 binding upstream (no. 32) or downstream (no. 33) of the stem loop structure. For PCR, these two reverse primers were combined with a pop forward primer (no. 31). L, 1 kb plus DNA Ladder (NEB); 32: PCR with primers 32 + 31; 33: PCR with primers 33 + 31; d. ORFs, downstream ORFs.