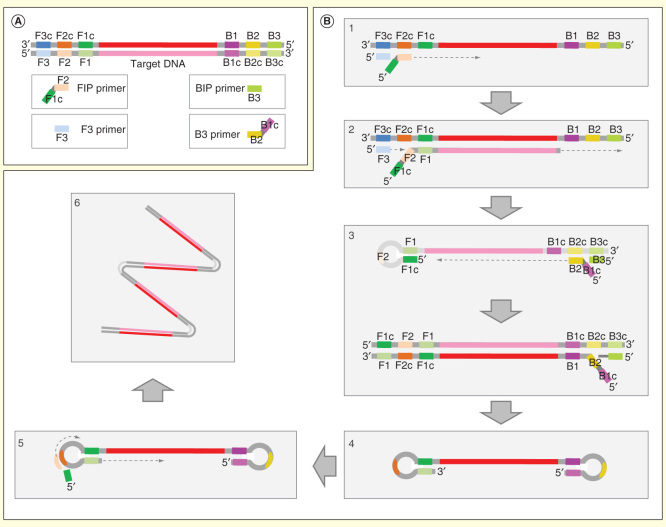
Figure 1.
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification. For clarity, only the process initiated in one strand is shown. (A) Primer design with inner primers (F1c-F2 and B1c-B2) and outer primers (F3 and R3). Loop primers are not shown. (B) Amplification process. (1) F2 region of the FIP primer anneals with DNA template by its homologous sequence (F2c) and strand extension take place by the polymerase. (2) DNA polymerase synthesizes a new strand from F3 and displaces the previous DNA strand. (3) F1c segment of F3 primer hybridizes with F1. At other end, B3 and BIP primers hybridize with their homologues sequences and process 1 and 2 are repeated. (4) Formation of loop DNA molecule. (5) DNA molecule steam loops on both ends enter in a cycling step and a concatemere final product with several inverted repeats is produced (6).
Image adapted from Eiken Genome site (http://loopamp.eiken.co.jp/e/lamp/principle.html).