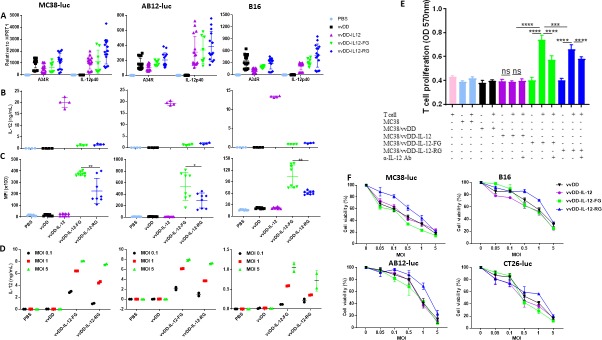
Figure 1.
Tethered IL-12 variants show functional IL-12 membrane association and similar cytotoxicity. (A) Tumor cell MC38-luc (3×105 cells), B16 (2×105 cells), or AB12-luc (3×105 cells) were mock-infected or infected with vvDD, vvDD-IL-12, vvDD-IL-12-FG, or vvDD-IL-12-RG at an MOI of 1. The cell pellets were harvested to measure A34R or IL-12 expression at 24 hours using RT-qPCR. The culture supernatants were harvested to measure secreted IL-12 using ELISA (B) and the cell pellets were also harvested to measure membrane-bound IL-12 using flow cytometry (cell surface staining) (C) 24 hours post-infection. (D) MC38-luc (3×105 cells), B16 (2×105 cells), or AB12-luc (3×105 cells) were mock-infected or infected with vvDD, vvDD-IL-12, vvDD-IL-12-FG, or vvDD-IL-12-RG at MOIs of 0.1, 1, and 5. The cell pellets were harvested to measure membrane-bound IL-12 using ELISA after PI-PLC cleavage 24 hours post-infection. (E) Naïve B6 splenocytes were activated and stimulated with IL-12 variant-infected MC38 cells (Responder: stimulator=1:5) in the absence/presence of α-IL-12 Ab, and T cell proliferation was measured using MTT assay 48 hours after coculture. (F) MC38-luc (1×104 cells), B16 (5×103 cells), AB12-luc (5×103 cells), or CT26-luc (1×104 cells) were infected with IL-12 variants at indicated MOIs and cell viability was measured using Cell Counting Kit-8 or MTS assay 48 hours post-infection. Data represent two independent experiments. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001; and ****P<0.0001. MOI, multiplicityof infection; NS, not significant; PI-PLC, phosphatidylinositol-specificphospholipase C.