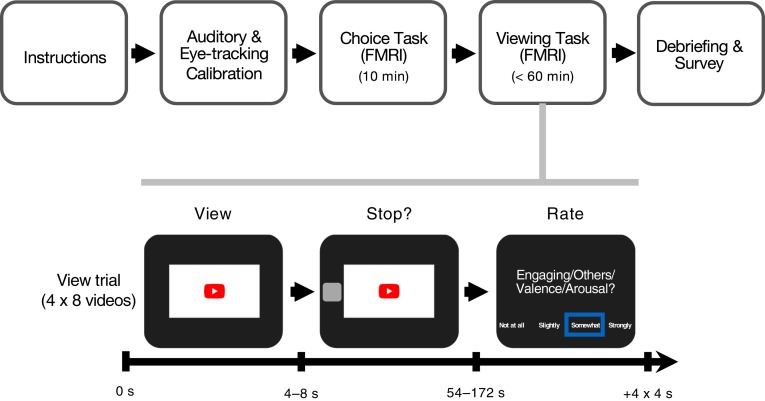
Fig. 1.
Viewing task procedure and trial structure. Participants received instructions and underwent auditory and eye-tracking calibration. During scanning, they saw thumbnails of each of the videos and indicated whether they wanted to view the video (video choice task); then, they were forced to watch at least 4 s of each video before responding to an option to stop watching the video, after which they rated the video on four scales (video viewing task). Finally, participants completed a debriefing survey (Upper). In video viewing task trials, participants watched each video (4 to 8 s), saw a prompt that allowed them to stop watching (stop), and rated four aspects of the video sequentially (engaging for self, engaging for others, valence, and arousal; 4 s each; Lower).