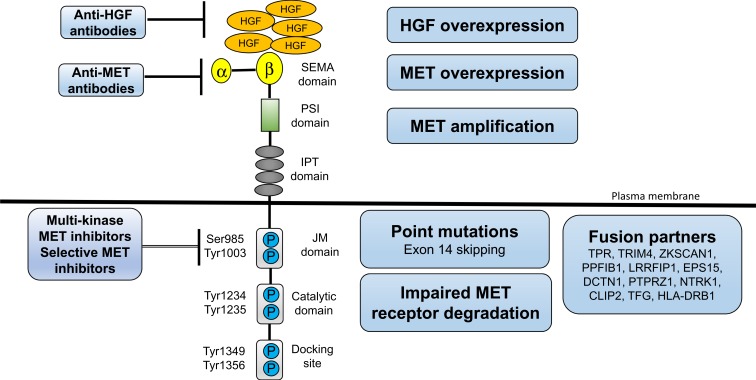
Figure 1.
Major Mechanism of MET/HGF axis dysregulation. The extracellular portion of c-MET consists of a four immunoglobulin (Ig)-like modules, a cysteine-rich, MET-related sequence domain, and a Sema domain (homologous to semaphorin) responsible for binding to HGF. The intracellular portion of c-MET consists of the paramembrane domain, the Catalytic domain, and the Docking site responsible for signal transduction. Various mechanisms of MET/HGF axis addiction in NSCLC, including MET/HGF overexpression, and MET gene alterations (including point mutations, amplification, and fusion). A number of drugs targeting MET (small molecule TKIs, MET antibody, and HGF antibody) have been studied. MET, c-mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer.