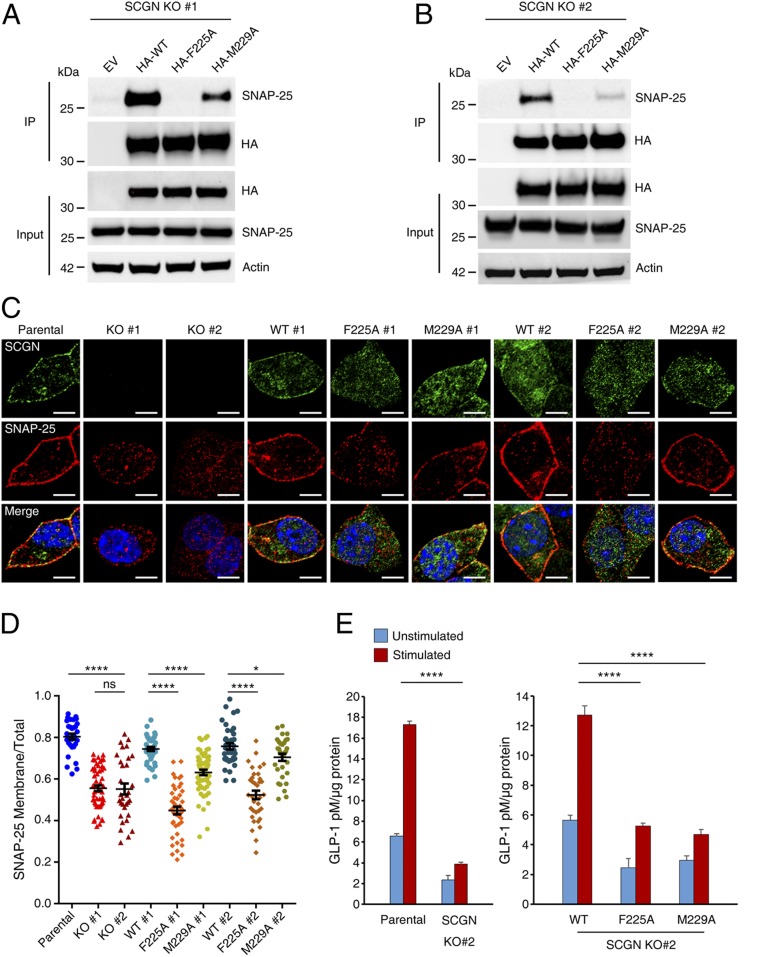
Fig. 5.
SCGN controls SNAP-25 subcellular localization and optimal hormone secretion in EECs in a SNAP-25–dependent manner. (A and B) Coimmunoprecipitation (Co-IP) analyses of two SCGN KO STC-1 clones stably expressing N-terminal HA-tagged human wild-type SCGN, SCGN (F225A, M229A) point mutant variants, or empty vector (EV). Cell lysates were precipitated with anti-HA affinity matrix, and probed with anti–SNAP-25 antibody. (C) Parental, two SCGN KO clones, as well as their rescue STC-1 cells were costained with anti-SCGN and anti–SNAP-25 antibodies. Representative cells are shown. (Scale bars, 10 µm.) Blue: DAPI staining. (D) Quantification of SNAP-25 membranous and total cellular fluorescence intensity ratio was calculated from each of the cell lines used in C. On average ∼40 cells were used for analysis in each group. Bars, mean; error bars, SEM; differences among groups by unpaired Student t test. *P < 0.05; ****P < 0.0001; ns, not significant. (E) GLP-1 release assay. Parental, SCGN-KO clone #2 and rescue STC-1 cells seeded on 6-cm dishes were treated with 100 µM DHA or Hepes buffer for 15 min. Supernatants were collected for analysis and values were normalized to protein concentration. Error bar, SEM; differences among stimulated groups using unpaired Student t test. ****P < 0.0001.