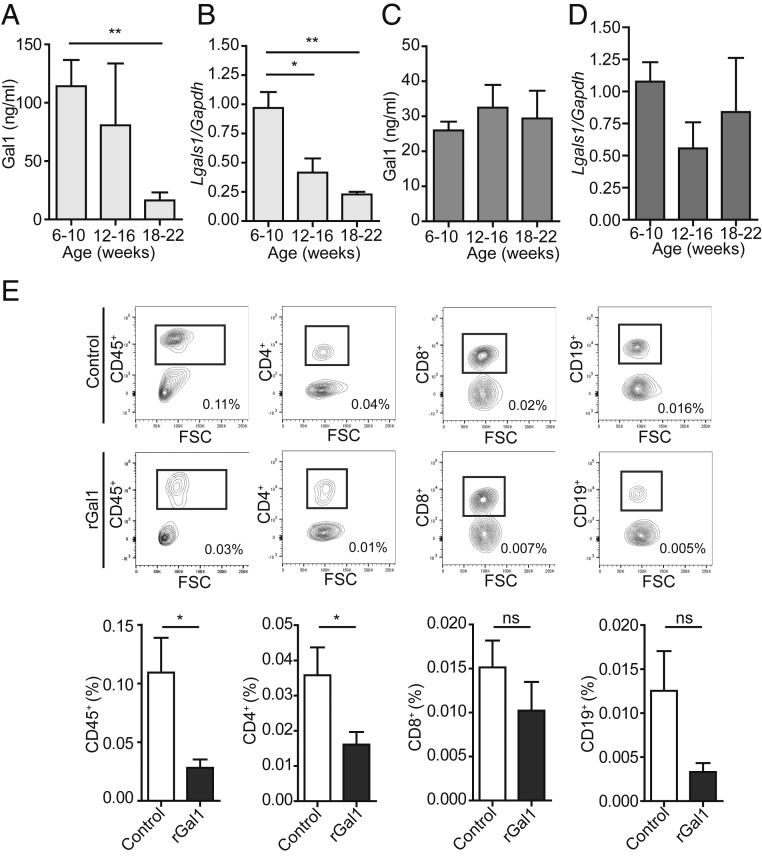
Fig. 5.
Age-dependent reduction of Gal1 expression in autoimmune-prone NOD mice. (A–D) Determination of Gal1 expression in serum and salivary glands of NOD and BALB/c mice (6 to 10, 12 to 16, and 18 to 22 wk old). ELISA for Gal1 in serum samples of NOD (A) and BALB/c (C) mice (n = 5 per group) and RT-qPCR analysis of Gal1 expression in submandibular salivary glands (n = 4 per group) from NOD (B) and BALB/c (D) mice (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, Student’s t test). (E) Frequency of infiltrating CD45+, CD4+, CD8+, and CD19+ cells in submandibular salivary glands of NOD (16 wk old) mice treated with rGal1 (100 µg) or PBS (six injections every 2 d). (Upper) Representative dot plots showing gating strategies used to quantify the frequency of CD45+, CD4+, CD8+, and CD19+ cells; the value shown on the graph represents the percent value of infiltrating cells with respect to whole salivary gland cells. (Lower) The average percentage of infiltrating cell populations with respect to the whole salivary gland (mean ± SEM, n = 5). A representative of three independent experiments is shown (*P < 0.05, Mann–Whitney test).