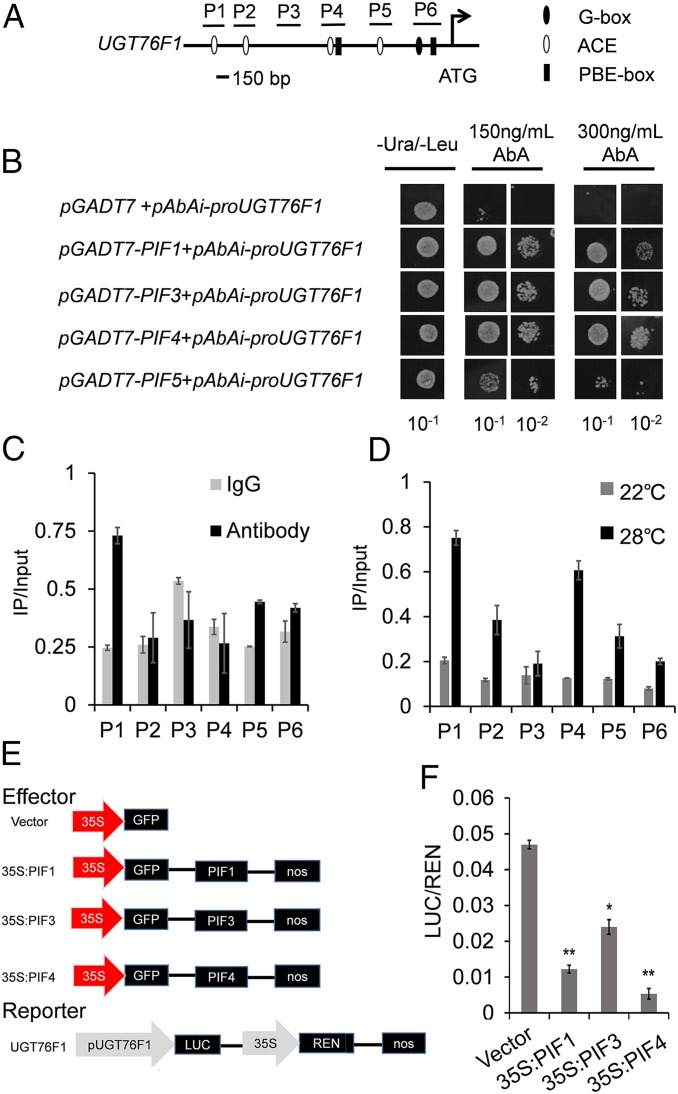
Fig. 3.
PIF4 is the major regulator for transcription activity of UGT76F1. (A) Promoter structure of the UGT76F1 gene and fragments used in the ChIP assay. The G box, ACE, and PBE box on sense strand of the UGT76F1 promoter are indicated by solid ovals, empty ovals and solid bars, respectively. P1–P6 indicate the promoter regions containing the above sequence or not, which were used in the ChIP/qPCR assay. (B) Yeast one-hybrid binding assay involving PIF1, PIF3, PIF4, PIF5, and UGT76F1 promoter. (C and D) ChIP-qPCR assay indicated that PIF4 is associated with the promoters of UGT76F1. Graphs show the ratio of bound promoter fragments (P1 to P6) versus total input detected by qPCR after immunoprecipitation. Mouse IgG was used as a mock control. Input sample was used to normalize the qPCR results in each ChIP. Data are means ± SD. n = 3. The experiments were repeated twice with similar results. (E and F) PIF4 transcriptionally activates the promoter of UGT76F1 in Arabidopsis protoplasts via transient dual-luciferase assays. The LUC-to-REN ratio indicates the activity of the transcription factors on the expression level of the promoters. LUC: firefly luciferase activity; REN: Renilla luciferase activity. Data are means ± SD. n = 30. Significant difference was compared to control. Student’s t test was performed (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01).