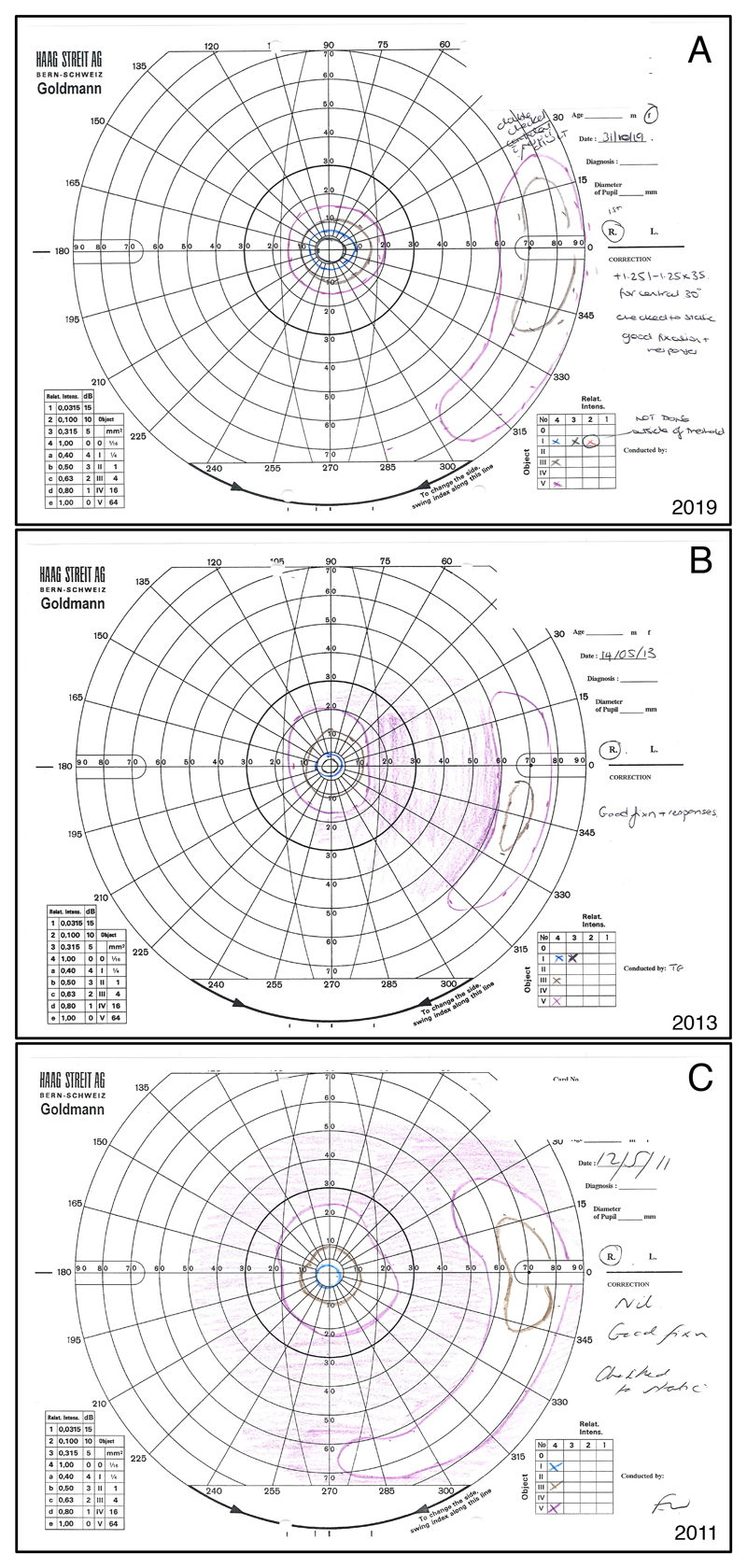
Figure 1.
Goldmann visual fields of the right eye of a 37 year-old female with PDE6B associated autosomal recessive RP. Figure 1A shows the most recent visual field from 2019, while 1B is from 2013, and 1C from 2011. The normal Goldmann visual field usually reaches about 90° temporally, 50° nasally, and 50-60° superiorly and inferiorly for the largest and brightest stimulus. All fields show a concentric constriction with a peripheral remnant of visual field, which is typical for RP. Significantly increased constriction and decrease in the size of the peripheral remnant can be noted from 2011 to 2013. However, the visual field from 2019 seems to not have worsened in comparison to the previous exams. Indeed, both the central island and the peripheral remnant appear larger. A test-retest variability of up to 20% even when using a single experienced operator has been known for Goldmann visual fields, and might explain the apparent improvement in visual field seen in this patient. The clinical improvement seen in the cystoid macular oedema between 2013 and 2019 (not shown) could however have contributed to a real improvement in visual field sensitivity in this case.
The purple lines represent the Goldmann stimulus V4e. The Roman number indicates the stimulus size of 64mm2 for V. The Arabic number and the lower case letter indicate the light intensity of 1000 apostilb (315 cd/m2). Brown = III4e (4mm2, 1000 asb); blue = I4e (1mm2, 1000 asb); black = I3e (1mm2, 315 asb).