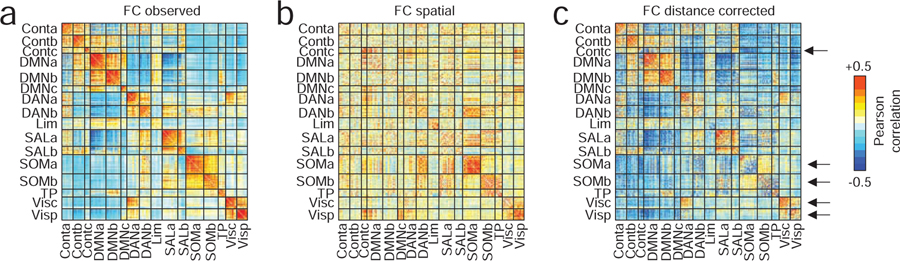
FIG. 2. Differences in correlation structure.
(a) The original (uncorrected) inter-regional correlation matrix ordered by cognitive system. (b) The correlation matrix obtained from the optimal spatial null model. (c) We correct for space-induced inter-regional correlation structure by subtracting the spatial null model matrix from the original matrix. Here, the arrows are used to draw attention to salient changes. The top arrow, for instance, shows that after correcting for distance, regions within the “Contc” system become weakly connected to each other. Similarly, in the original network, the correlation magnitude within somatomotor and visual systems are among the strongest across the brain. As with the control network component, these systems exhibit marked reductions in their internal connection strength following correction.