Figure 1.
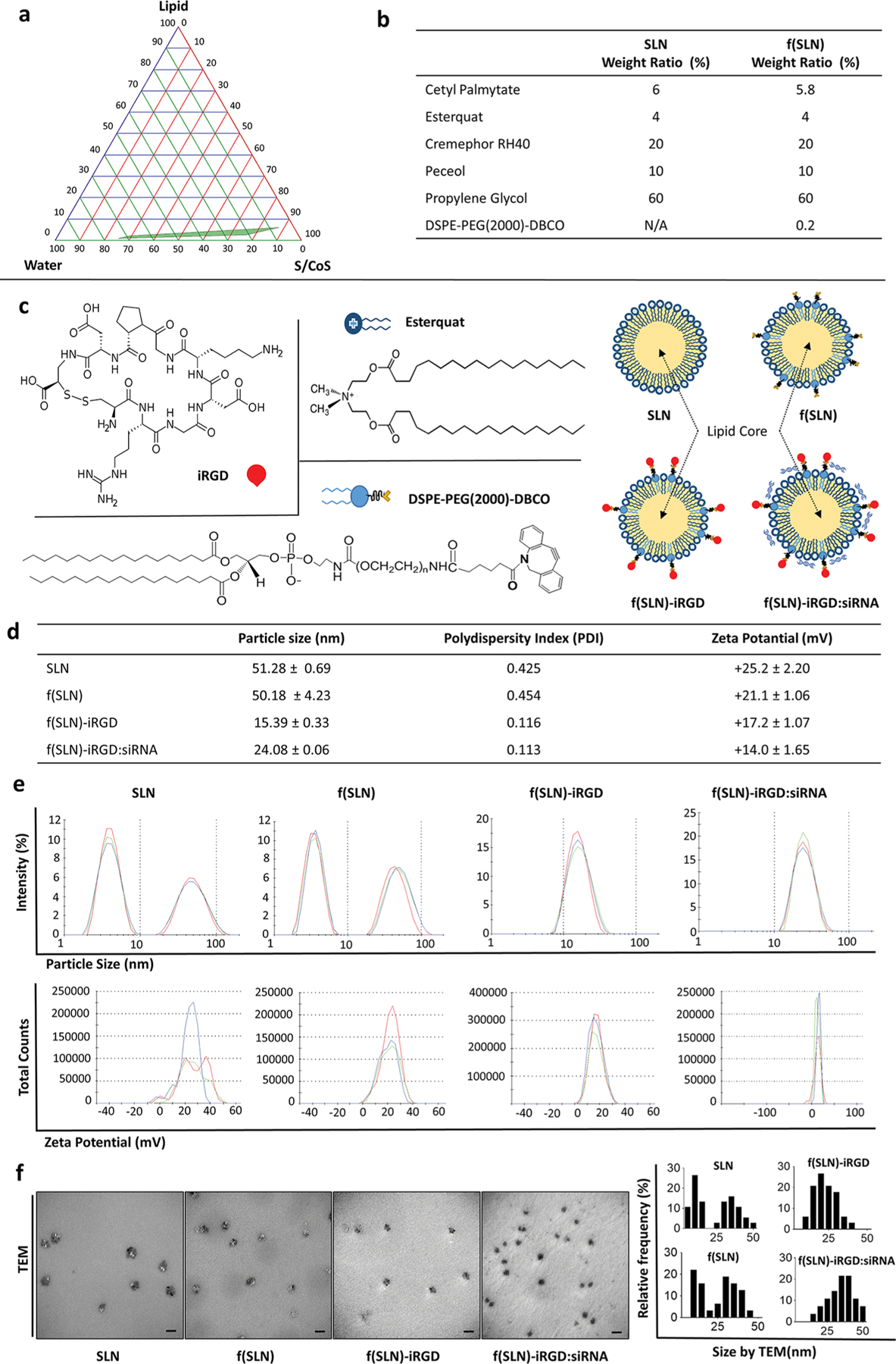
Construction and characterization of f(SLN)-iRGD:siRNA for targeted glioblastoma therapy. (a) Pseudoternary phase diagram for the microemulsion system formed with lipid (cetyl palmitate), surfactant/cosurfactant (S/CoS; cremephor RH 40+peceol/propylene glycol), and water (UPH2O); green area represents transparent o/w microemulsion formation region. (b) Weight ratio of the different components of SLN and f(SLN). (c) Chemical structure of DSPE-PEG(2000)-DBCO, Esterquat, and iRGD peptide with schematic overview of SLN, DSPE-PEG(2000)-DBCO containing functionalized SLN [f(SLN)], iRGD-targeted f(SLN) [f(SLN)-iRGD], and targeted f(SLN) complexed to siRNA [f(SLN)-iRGD:siRNA]. (d) Characterization of SLN, f(SLN), f(SLN)-iRGD, and f(SLN)-iRGD:siEGFR. (e) Size and ζ-potential distribution of SLN, f(SLN), f(SLN)-iRGD, and f(SLN)-iRGD:siEGFR; blue, green, and red represent different measurements for the same nanoparticle. (f) Transmission electron micrograph (left) and size distribution of each nanoparticle analyzed by ImageJ (right); scale bar, 100 nm.
