Fig. 5.
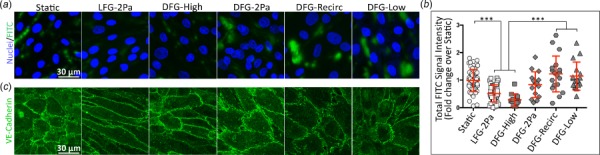
Endothelial monolayer permeability increased in lower shear stress disturbed flow regions. (a) Confocal microscopy images (63×) of FITC–streptavidin (green) permeation through an endothelial monolayer, with labeled nuclei (bisbenzimide, blue). Confluent BAEC monolayers grown on biotin-conjugated gelatin were exposed to various flow regimes for 36 h. Monolayers were then incubated with streptavidin-conjugated FITC, which diffused through leaky monolayers to bind to the culture surface via powerful biotin–streptavidin interactions. (b, left) FITC signal after thresholding to remove noise indicates pixels-of-interest surface area without brightness. (b, right) Total FITC fluorescence intensity quantification (161 images among 24 samples, across 4 independent experiments). *** indicates p < 0.0001.
