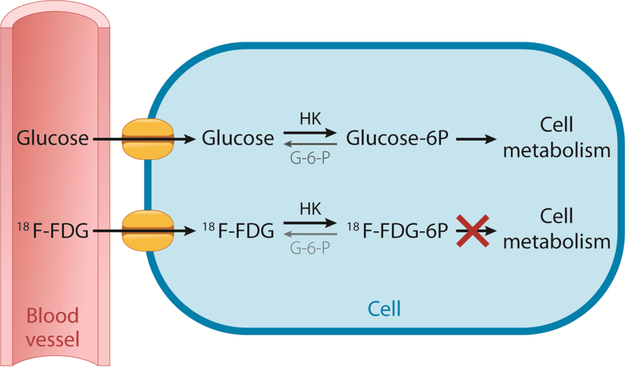
Fig. 1.
Glucose and 18F-FDG Cellular Uptake and Metabolism. Both glucose and 18F-FDG enter the cells by glucose transporter membrane proteins. Once in the cell, both are phosphorylated by hexokinase (HK), which can be reversed by glucose-6-phosphatase (G-6-P) if present. Phosphorylated glucose (Glucose-6 P) is available to be further metabolized by the cell, whereas phosphorylated 18F-FDG (18F-FDG-6 P) cannot be further metabolized and is therefore considered “trapped”.