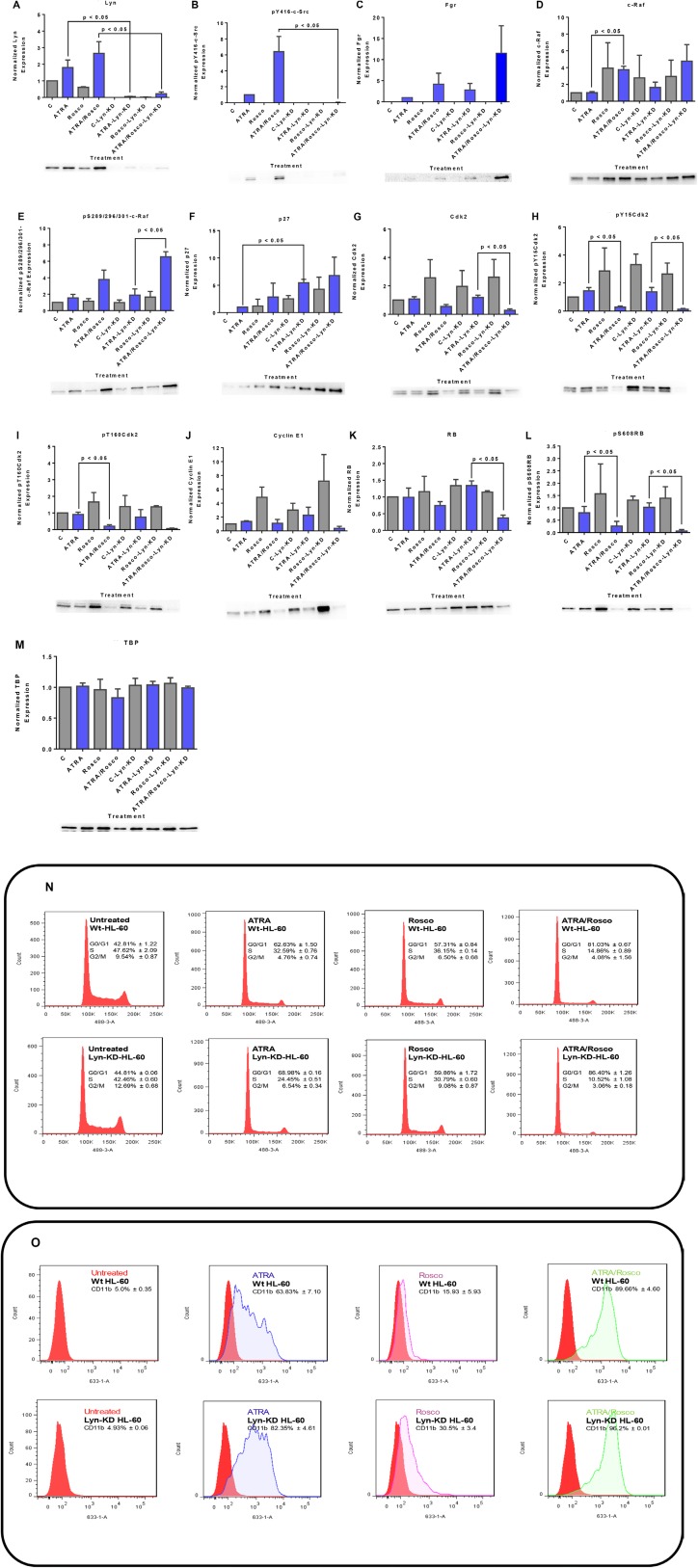
Figure 7. Western blots of nuclear lysate, CD11b and DNA histograms show that Lyn knockdown enhances ATRA-roscovitine induced gene expression and myeloid differentiation.
(A, B) ATRA and ATRA plus roscovitine co-treated Lyn KD cells caused a modest increase in Lyn and the phospho-residue, pY416-c-Src, expression. (C) Lyn knockdown enhances Fgr expression in Lyn KD cells co-treated with ATRA and roscovitine. (D, E) Lyn knockdown enhances c-Raf and phospho- S289/296/301-c-Raf expression in Lyn KD cells co-treated with ATRA and Roscovitine (F). p27Kip1 protein expression upregulates in Lyn KD cells co-treated with ATRA and roscovitine (G–J). Total Cdk2, phospho-Cdk2Y15, phospho-Cdk2T160 and cyclin E1 downregulates in Lyn KD cells co-treated with ATRA and roscovitine (K, L). Cotreatment of Lyn KD cells also deceases total RB expression and induced hypophosphorylation at serine 608 (S608) of RB (M). TATA binding protein (TBP) was used as loading control. p < 0.05 comparing ATRA-treated samples to ATRA/Roscovitine-treated samples of either wild-type and Lyn-KD cells. (N) Cell cycle distribution showing the percentage of cells in G1/G0, S and G2/M was analyzed using flow cytometry with propidium iodide. ATRA/roscovitine-induced differentiation of Lyn KD stable cells marked by G1/G0 cell cycle arrest was enhanced compared to parental wild type cells. (O) CD11b expression assessed by flow cytometry with an APC-conjugated antibody. Lyn KD cells show enhanced CD11b expression in response to ATRA when compared to wild-type cells. Also, a difference in CD11b expression was found between ATRA/roscovitine-treated parental wild type and Lyn KD cells. All experiments shown are representative of three replicates..