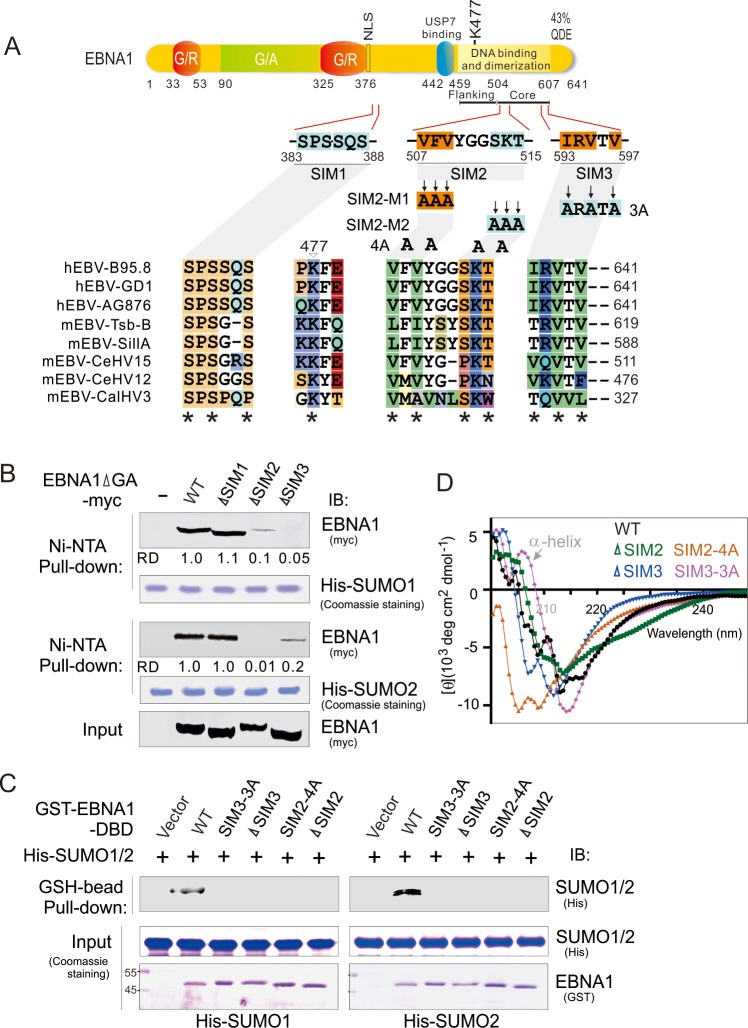
Fig 1. EBNA1 contains two SUMO-interacting motifs.
(A) Schematic representation of different EBNA1 mutants with mutation of SUMO-interacting motifs (SIMs). The residue positions of each putative SIM1, SIM2, and SIM3 of EBNA1, site-mutation of four SIM mutants (SIM2-m1, SIM2-m2, SIM2-4A, and SIM3-3A), and G/A and G/R rich region are indicated. K477 is the putative SUMOylation site based on SUMOplotanalysis. The amino acid alignment of SIM regions of EBNA1 homologs encoded by different EBV strains of human and other primate is shown at the bottom panel. The asterisk indicates highly conserved residues. QDE, acidic domain. NLS, nuclear localization sequence. (B) The SIM2 and SIM3 of EBNA1 are required for interaction with SUMO1/2. HEK293T cells were individually transfected with expression plasmids as indicated in the figure. At 48 h post-transfection, whole cell extracts (Input) were subjected to a pulldown with His-SUMO1 or His-SUMO2 recombinant proteins with Nickel-agarose (Ni-NTA) beads, followed by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-myc antibodies. His-SUMO1 and His-SUMO2 recombinant proteins are shown by Coomassie staining. The relative density (RD) of EBNA1-interacting SUMO1 or SUMO2 is quantified and shown on the right panel. Input was used at 5%. (C) The SIM2 and SIM3 motifs of EBNA1 are required to directly bind with SUMO1/2 in vitro. Equal protein amounts of purified His-SUMO1/2 (Input) were individually incubated with wild type (WT) EBNA1 and its SIM2/3 mutants of GST-fusion proteins purified from E.coli expression system and pulled down with Glutathione (GSH)-sepharose beads. Bound complexes were analyzed by immunoblotting (IB) with the indicated antibodies. The recombinant proteins are shown by Coomassie staining at the bottom panel. (D) Circular dichroism (CD) spectra for wild type EBNA1 and its SIM2/3 mutants in phosphate buffer (pH = 7.2).