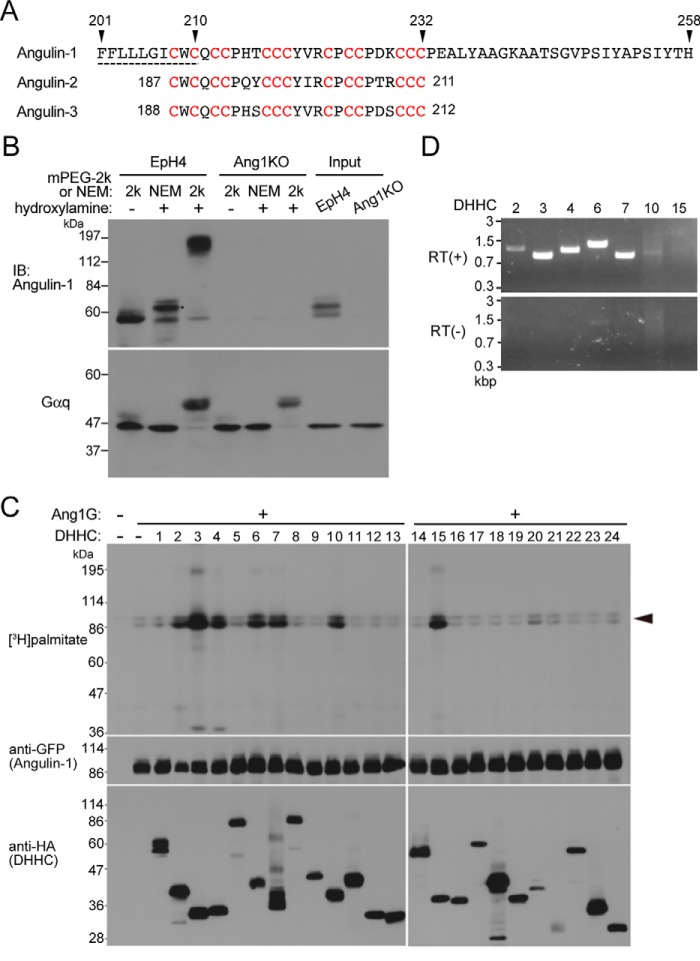
Figure 2.
Palmitoylation of angulin-1. A, amino acid sequence of the last half of the transmembrane domain and the following juxtamembrane region of mouse angulin-1 (GenBankTM AK146807). The predicted transmembrane domain is shown by the dashed line. The 13 cysteine residues (red) within amino acids 208–232 of angulin-1 are conserved within amino acids 187–211 of angulin-2 (GenBankTM K136284) and amino acids 188–212 of angulin-3 (GenBankTM FJ024498). B, palmitoylation of endogenous angulin-1 in EpH4 cells detected by the APEGS method. After the reduction and alkylation of free cysteine thiols of proteins in cell lysates, palmitoyl-thioester linkages of the protein palmitoylation sites in cell lysates are cleaved by hydroxylamine treatment, and newly formed thiols are labeled with mPEG-2k. As a negative control, NEM of 125 Da was added instead of mPEG-2k. The rightmost two lanes show the results for the original lysates without any treatments. The remarkable mobility shift of angulin-1 in the hydroxylamine(+)/mPEG-2k lane compared with the negative control lanes, hydroxylamine(−)/mPEG-2k and hydroxylamine(+)/NEM, in EpH4 cells demonstrates that angulin-1 is highly palmitoylated. The mobility shift observed in the hydroxylamine(+)/NEM lane compared with the hydroxylamine(−)/mPEG-2k lane (asterisk) is probably caused by the addition of NEM (125 Da) to multiple palmitoyl cysteine residues. Because replacement of a palmitoyl group (239 Da) with NEM reduces the molecular weight of angulin-1, the slower mobility of the hydroxylamine(+)/NEM sample may be caused by structural change of angulin-1 protein by the NEM blinding. The bottom panel shows immunoblotting of the corresponding samples with an anti-Gαq antibody as a positive control for protein palmitoylation. IB, immunoblotting. C, screening for DHHCs responsible for palmitoylation of angulin-1. Each DHHC family member with an HA tag was cotransfected with Ang1G into HEK293T cells. After metabolic labeling with [3H]palmitate, proteins in the cell lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE and subjected to autoradiography and immunoblotting with anti-GFP and anti-HA antibodies. The results are representative of two independent experiments. D, expression of DHHC transcripts in EpH4 cells. The expression of DHHCs capable of Ang1G palmitoylation in C was analyzed by RT-PCR using total RNA from EpH4 cells as a template. RT(+) and RT(−) indicates reverse transcriptase–positive and –negative reactions, respectively.