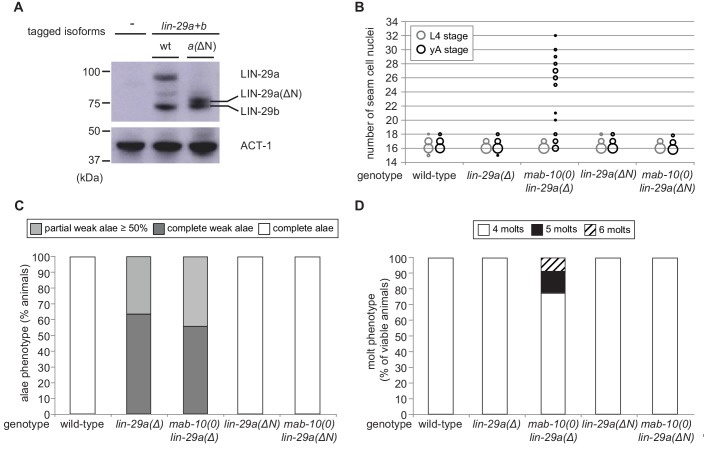
Figure 6. The LIN-29a-specific domain is dispensable for the execution of the J/A transition.
(A) Western blot of endogenous C-terminally GFP::3xFLAG-tagged LIN-29a and LIN-29b proteins in the lin-29a(ΔN) background (HW2408) using an anti-FLAG antibody. Actin-1 is used as loading control. (B) Seam cell number quantification in L4 larval stage and young adult (yA) animals of the indicated genetic backgrounds (n > 25 for L4, n > 25 for yA worms per genotype). The data for lin-29a(Δ) and mab-10(0) lin-29a(Δ) is re-plotted from Figure 2 for comparison. (C) Quantification of different alae structures in young adult worms of indicated genotypes (n > 20). The data for lin-29a(Δ) and mab-10(0) lin-29a(Δ) is re-plotted from Figure 3 for comparison. (D) Quantification of the number of molts for animals of indicated genotypes (n > 20). The data for lin-29a(Δ) and mab-10(0) lin-29a(Δ) is re-plotted from Figure 3 for comparison. In (B – D), lin-29(∆N) is lin-29(xe200).