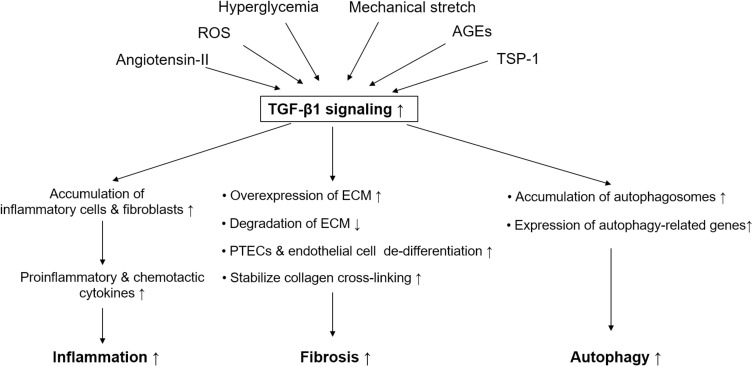
FIGURE 1.
Simplified schematic diagram of pathological role of TGF-β1 signaling in diabetic kidney disease. Pathogenic stimuli in diabetic kidney disease like hyperglycemia, angiotensin-II, reactive oxygen species, mechanical stretch, advanced glycation end products, and thrombospondin-1 are able to active TGF-β1 signaling. TGF-β1 signaling plays an important role in mediating renal fibrosis, inflammation, and autophagy in proximal tubular epithelial cells in diabetic kidney disease. TGF-β, transforming growth factor-beta; ROS, reactive oxygen species; PTECs, proximal tubular epithelial cells; AGE, advanced glycation end products; TSP-1, thrombospondin-1; ECM, extracellular matrix.