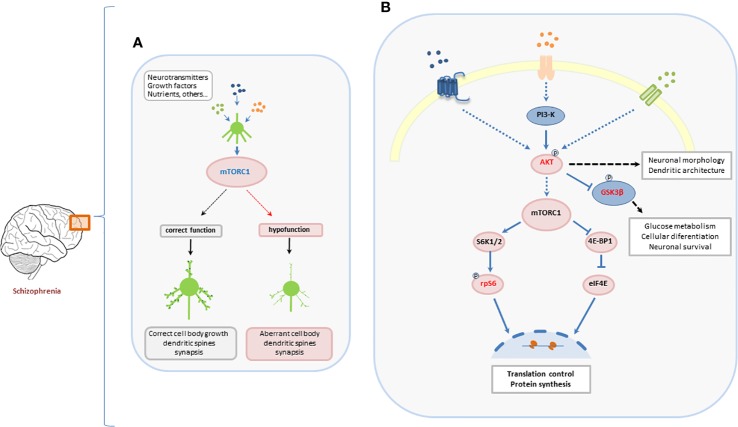
Figure 3.
Suggested role of mTORC1-dependent signaling pathway in the development of neurons and its implication in aberrant development of PFC in schizophrenia. (A) Neurotransmitters, growth factors, nutrients, and other environmental inputs coordinately activate mTORC1 leading to a correct normal neuronal development. Hypofunction of mTORC1 induces a dysregulation of the neuronal development that may be involved in the development of psychiatric disorders. (B) The canonical Akt/mTORC1/S6 pathway. The two main targets of mTORC1, S6K, and 4E-BP1, are involved in the translational machinery for protein synthesis. Once active, S6K regulates the activity of the ribosomal protein S6 by phosphorylating it at different sites. The phosphorylation of S6 controls translation and regulates protein synthesis in the central nervous system (CNS).