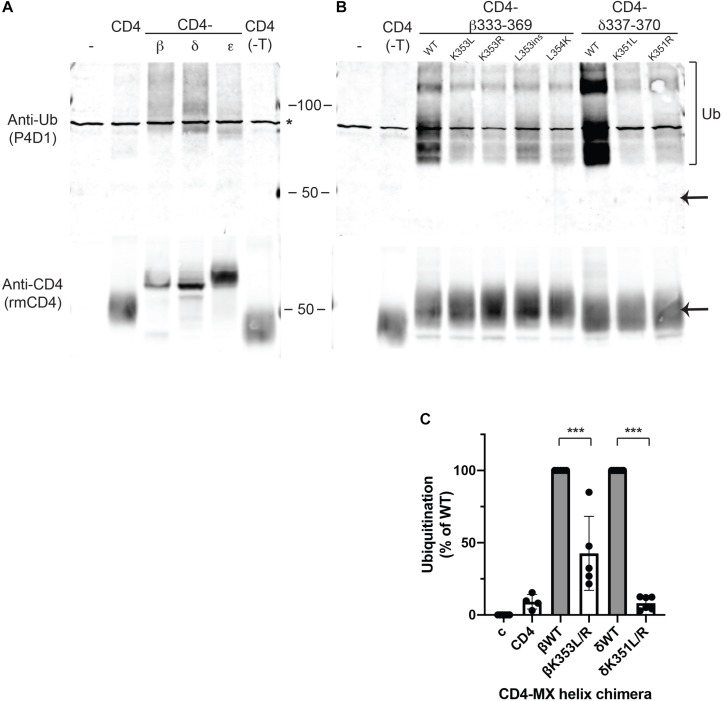
FIGURE 3.
Retention is associated with ubiquitination of MX-helix lysine residues. (A,B) CD4 subunit loop chimeras expressed in HEK cells were immunoprecipitated from cell extracts using anti-CD4 antibody cross-liked to agarose beads. The isolates were immunoblotted with monoclonal anti-ubiquitin antibody (P4D1), and then re-probed with polyclonal anti-CD4 antibody. We detected ubiquitination of both CD4-β and δ full loops (A) and CD4-β333-369 and δ337-370 MX-helix chimeras (B). The ubiquitination was evident as a characteristic ladder of high molecular weight forms (bracket) beginning around 9 kD above the major band detected with anti-CD4 antibody (arrow). In contrast, little or no ubiquitination was evident for CD4 (control), CD4 with a deleted intracellular tail (CD4-T), or CD4-ε loop. Note that the asterisk marks a non-specific band present in non-transfected samples. (B) High levels of ubiquitination of CD4-β333-369 and δ337-370 were greatly reduced by mutation of βK353 or δK351 to either leucine (L) or arginine (R). Mutations adjacent to βK353 also reduced ubiquitination (βL353ins and βL354K). (C) Quantification of the immunoblots shows that ubiquitination of CD4-β333-369 was reduced 57% by K353L/R mutations, and ubiquitination of CD4-δ337-370 was reduced 92% by K351L/R mutations (***p < 0.001, one way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison’s test, n = 4–6 independent transfection experiments).