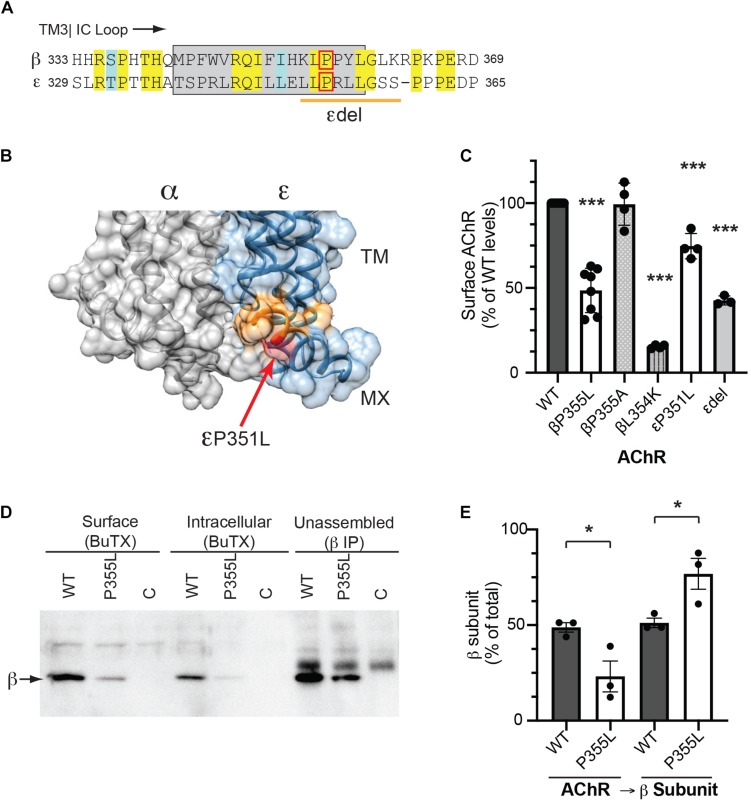
FIGURE 5.
CMS-linked mutations in the MX-helix impair AChR assembly and expression. (A) Sequence alignment showing the initial portion of the beta and epsilon cytoplasmic (TM3-TM4) loops, with the MX-helix shown by the gray box. The two CMS-linked mutations in the epsilon subunit are denoted by the red box (εP351L) and orange line (εdel349-357), respectively. The analogous proline in the β subunit MX-helix (βP355L) is indicated by the red box. (B) Molecular structure showing the cytoplasmic interface between the alpha and epsilon subunits. The end of the ε MX helix contacts the short loop connecting TM3 to the MX-helix of the α subunit. Residues deleted in the εdel mutation are shown in orange and the εP351L mutation is marked by the red arrow. (C) HEK cells were transfected with AChR in wild type form or with the indicated mutations in the MX-helix, and surface levels of AChR were measured by 125I-alpha-BuTx binding. Compared to WT AChR, the CMS-linked mutations in epsilon (εP351L and εdel349-357) decreased surface levels of AChR by 25 and 57%, respectively. The corresponding βP355L mutation decreased surface AChR by 51% but βP355A mutation had no discernable effect. Beta L354K mutation, which is predicted to misposition the MX helix, decreased surface AChR by 85% (***p < 0.0001 as compared to WT; one way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison’s test; n = 3–8 experiments). (D) HEK cells were transfected with wild type or βP355L-AChR. We then sequentially isolated surface AChR, intracellular AChR, and unassembled beta subunit, and immunoblotted with anti-beta subunit antibody to compare the levels in each pool. Significant amounts of wild type β subunit were detected in the pools of surface and intracellular AChR, as well as in the pool of unassembled subunit. In contrast, βP355L subunit was mostly detected in the unassembled subunit pool, indicating that it assembled less efficiently into AChR. (E) Quantification shows that a smaller percentage of P355L β subunit (23%) assembled into AChR compared to wild type β subunit (49%) (*p < 0.05, one way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison’s test, n = 3 experiments).