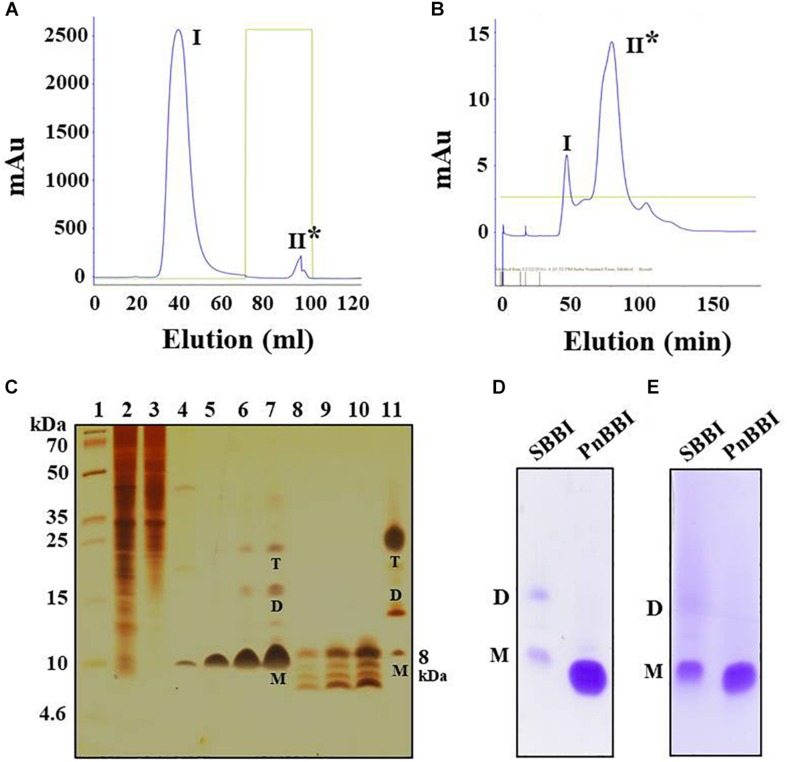
FIGURE 1.
Purification profile of PnBBI and its in-gel activity. Elution profile of (A) trypsin-Sepharose 4B column loaded with 20-60% (NH4)2SO4 active fraction; (B) Sephadex G-50 fine column loaded with active peak II fraction pool of trypsin affinity column; (C) Tricine SDS-PAGE (15%) showing purification profile and self-association pattern of PnBBI: lane 1, molecular weight marker designated in kDa; lane 2, peanut crude protein extract (20 μg); lane 3, 20-60% (NH4)2SO4 protein fraction (15 μg); lane 4, active fraction pool (Peak II) of trypsin affinity column (10 μg); lanes 5-7 and 8-10 active fraction pool (peak II) of gel filtration column under non-reducing and reducing conditions with increased protein concentration (2.5, 5, and 10 μg), respectively; lane 11, soybean BBI (5 μg) was used as a reference. Gelatin SDS-PAGE (15%): Lane 1, soybean BBI (5 μg); lane 2, PnBBI (5 μg) active against (D) bovine pancreatic trypsin and (E) chymotrypsin, respectively. Asterisks indicate active peak with inhibitory activity against trypsin. M-monomer, D-dimer and T-tetramer. The data shown here is the representative of three biological replicates (data provided as Supplementary Data Sheet 3).