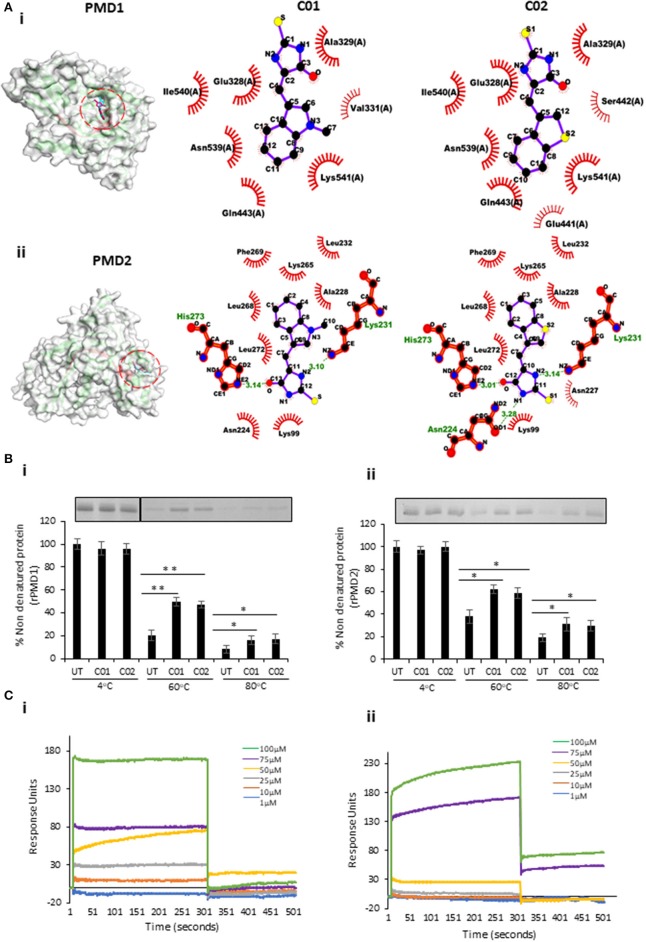
Figure 3.
In silico and in vitro interaction of C01 and C02 with rPMDs. (A) The PyMOL rendered surface structures of docked complexes have shown strong binding of C01 and C02 to the signature motif of PMD1 (i) and PMD2 (ii). The ligplot+ rendered scheme demonstrates strong interactions as shown by the close proximity between the C01 and C02 and hydrophobic amino acids (depicted by bold, eyelash-like structures), and hydrogen bonds formed with polar residues. (B) Interaction of PMIs and PMDs by CETSA. The drug-target engagement between the compounds and recombinant proteins was analyzed by subjecting the samples to thermal denaturation at 60 and 80°C (i) (ii). The protein intensity at 4°C was taken as control. The band intensities graph was plotted considering the 4°C samples as 100% non-denatured protein. UT indicates PMI untreated sample. Error bar represents SD (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01). (C) rPMD1 was immobilized onto a nickel charged NTA SPR chip. C01 (i) and C02 (ii) were injected over immobilized rPMD1. The PMIs show concentration-dependent binding to rPMD1 with a Kd value of 0.1183 ± 0.0370 and 0.0866 ± 0.0709 for C01 and C02, respectively.