Figure 2.
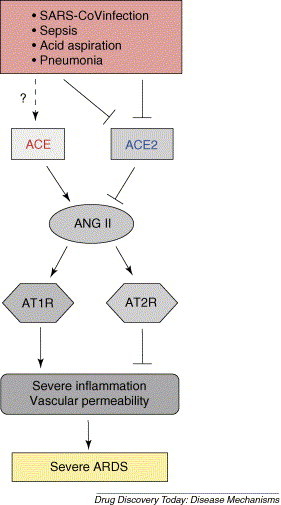
Schematic diagram of the proposed role of the renin–angiotensin system in development of ARDS. In ARDS induced by SARS-CoV infections, acid aspiration, pneumonias, sepsis or other pathogenic conditions, the generation of Ang II from Ang I is mediated by ACE. Ang II contributes to acute lung failure through stimulation of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R), whereas ACE2 and angiotensin II type 2 receptor (AT2R) negatively regulate this pathway and protect from acute lung failure. However, additional ACE2-regulated, but Ang II-independent pathways seem to also contribute to ARDS.
