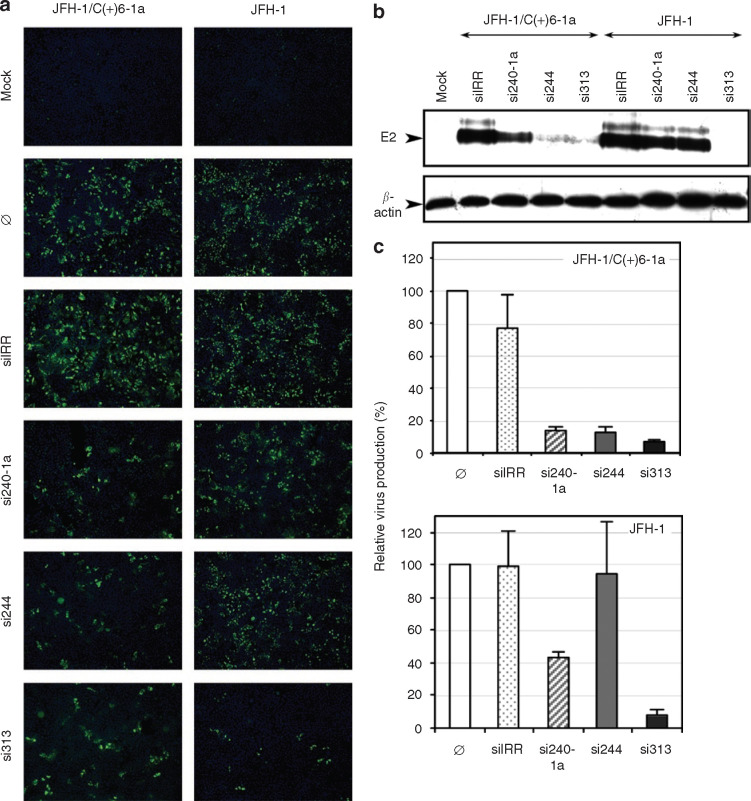
Figure 5.
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) 5′NTR-specific small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) silence virus replication in cell culture. (a) HuAP cells were transfected with no siRNA (Ø), irrelevant siRNA (siIRR) or the indicated HCV-specific siRNA (si240-1a, si244, si313), and then infected at 16 hours after transfection with either JFH-1 strain of HCV genotype 2a (right panels) or a chimeric JFH-1 virus containing 5′NTR-C sequences from the H77 strain of HCV genotype 1a (JFH-1/C(+)6-1a, left panels). At 42 hours post-infection (p.i.), cells were fixed and processed for core detection by immunofluorescence and counterstained with Hoechst dye to visualize nuclei. Overlaid images (×10) are shown. Control cells that were mock-transfected and mock-infected (Mock) were processed in parallel. (b) Extracts from siRNA-transfected and HCV-infected cells collected at 42 hours p.i. were analyzed by Western blotting for expression of E2 glycoprotein (upper gel) and cellular β-actin (lower gel) as loading controls. (c) Virus yields in supernatants from siRNA-transfected and HCV-infected cells collected at 42 hours p.i. were quantified in genome equivalents/ml by real-time quantitative RT-PCR and expressed relative to virus production in the absence of siRNA treatment, set at 100% (mean ± SD of duplicates in two independent experiments). NTR, nontranslated region; RT-PCR, reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction.