Figure 1.
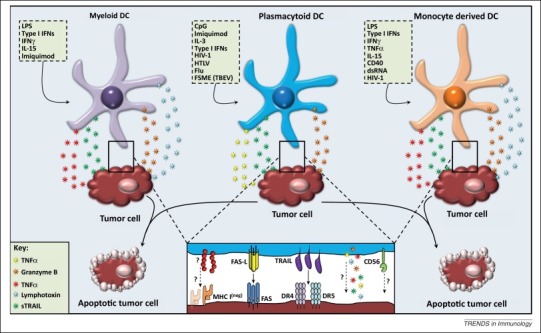
Direct cytotoxicity of human killer DC subsets. Activation of human DCs with various stimuli, for example, viruses, cytokines, TLR ligands, induces a cytotoxic function. DCs can exert their cytotoxic ability either by the secretion of soluble factors or by the expression of apoptosis inducing molecules. It is unclear whether soluble factors play a role at the contact site between target cells and DCs, how killer DCs recognize MHC-class-I-negative target cells, or if there is a role for CD56 in the cytotoxic function of killer DCs. Abbreviations: CpG, CpG oligodeoxynucleotides; DC, dendritic cell; dsRNA, double-stranded RNA; Flu, influenza; FSME, früh sommer meningo-encephalitis; HIV-1, human immunodeficiency virus 1; HTLV, human T lymphotrophic virus; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; sTRAIL, soluble tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand; TBEV, tick-borne encephalitis virus; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
