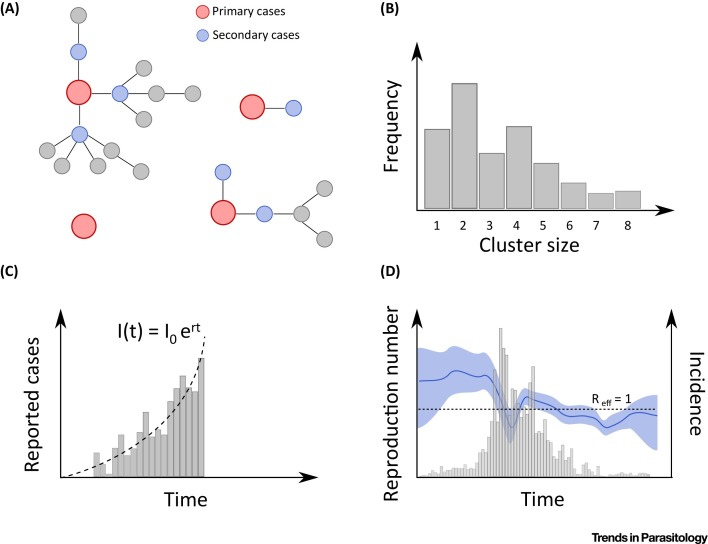
Figure 1.
Approaches to Estimate the Reproduction Number. (A) When chains of transmission are available, the reproduction number is obtained by counting directly the number of secondary infections. (B) The reproduction number can also be estimated from the distribution of the sizes of clusters of human cases. (C) Epidemic time series are also informative. At the start of an epidemic, the number of cases grows exponentially, and the growth rate r can be used to estimate of the reproduction number. (D) During the course of an epidemic, variations of the reproduction number can also be estimated.