Figure 2.
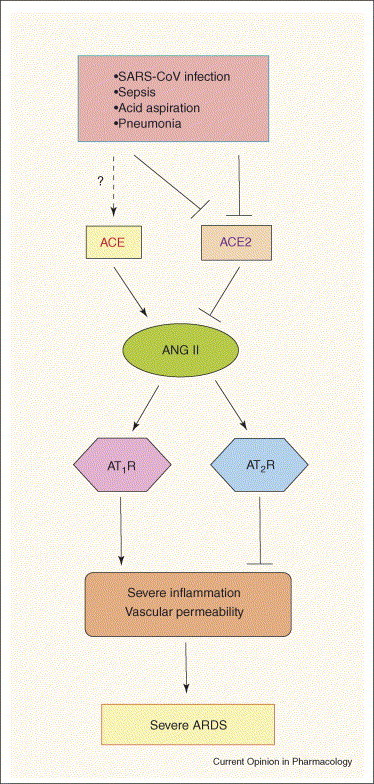
Schematic diagram of the proposed role of the RAS in development of severe ARDS. In acute lung injury such as SARS-CoV infections, acid aspiration, pneumonias or sepsis, the generation of ANG II from ANG I is enhanced by ACE. ANG II contributes to acute lung failure through stimulation of the AT1 receptor, whereas ACE2 and the AT2 receptor negatively regulate this pathway and protect from acute lung failure. However, additional ACE2-regulated, but ANG II-independent, pathways seem to also contribute to ARDS.
