Fig. 2.
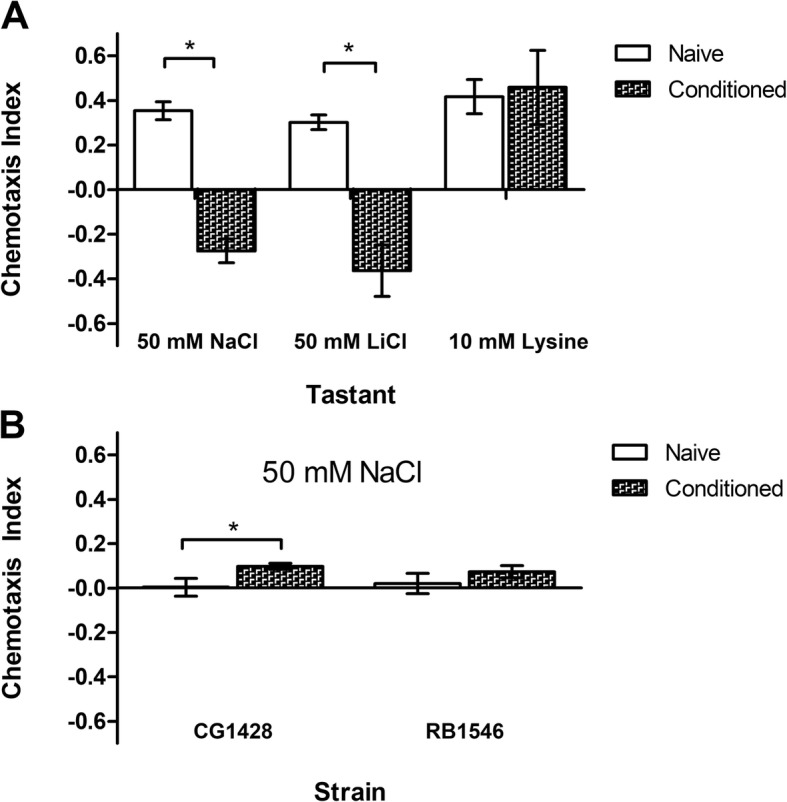
The effects of sodium conditioning on chemotaxis. Each individual chemotaxis assay contained at least 100 nematodes, data reported here as average of independent assays (n). Each data point represents a minimum of three assays. Nematodes were conditioned for 20 min in either CTX buffer or CTX buffer containing 50 mM NaCl. Chemotaxis index (C.I) has a range of − 1 to 1, where positives values indicate attraction to tastant, negative values indicate aversion, and values close to 0 indicate no preference. Error bars represent SEM. (a) Sodium conditioning disrupts wild-type nematodes’ NaCl and LiCl attraction pathway. Sodium conditioned N2 nematodes behaved significantly different from their naïve counterpart toward 50 mM NaCl (n: naïve = 6, conditioned = 5) and 50 mM LiCl (n: naïve = 4, conditioned = 4). There was no statistically significant difference in their behavior toward 10 mM lysine (n: naïve = 5, conditioned = 5). For this and panel B, asterisks identify significant conditioning effects as indicated by unpaired Student’s t-test (p < 0.05). (b).Tmc-1 mutation disrupts nematodes’ innate attraction and induced aversion to 50 mM NaCl. (n: CGnaïve = 5, CGconditioned = 5, RBnaive = 4, RBcondtioned = 4)
