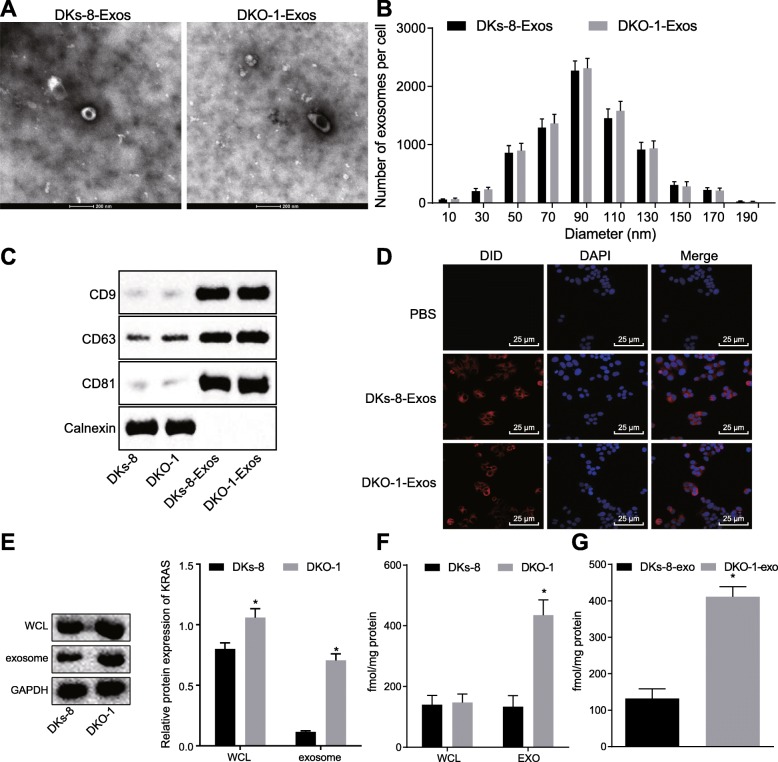
Fig. 3.
CRC cells transfer KRAS mutants to neutrophils via exosomes; a, DKs-8- and DKO-1-derived exosomes viewed under electron microscope; b, Size (diameter) distribution of DKs-8- and DKO-1-derived exosomes; c, The expression of exosome surface marker measured by Western blot analysis; d, Exosomes can be internalized by neutrophils revealed by Confocal microscopy (400×); e, The expression of KRAS in DKs-8 and DKO-1 cells (WCL) and their derived exosomes (EXO) measured by Western blot analysis; f, The presence of KRAS in DKs-8 and DKO-1 cells and their derived exosomes. Proteins from DKs-8 and DKO-1 cells (WCL) and their derived exosomes (EXO) were resolved via SDS-PAGE and subjected to targeted LC-MRM analysis for WT (LVVVGAGGVGK) and mutant (LVVVGAGDVGK) (G13D) KRAS peptides; g, mutant (G13D) KRAS in neutrophils LC-MRM detected by LC-MRM. * p < 0.05. The measurement data was expressed as mean ± standard deviation. An unpaired t test was used to compare the two groups. Data analysis at different time points was performed by repeated measurement ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test. The experiment repeated three times