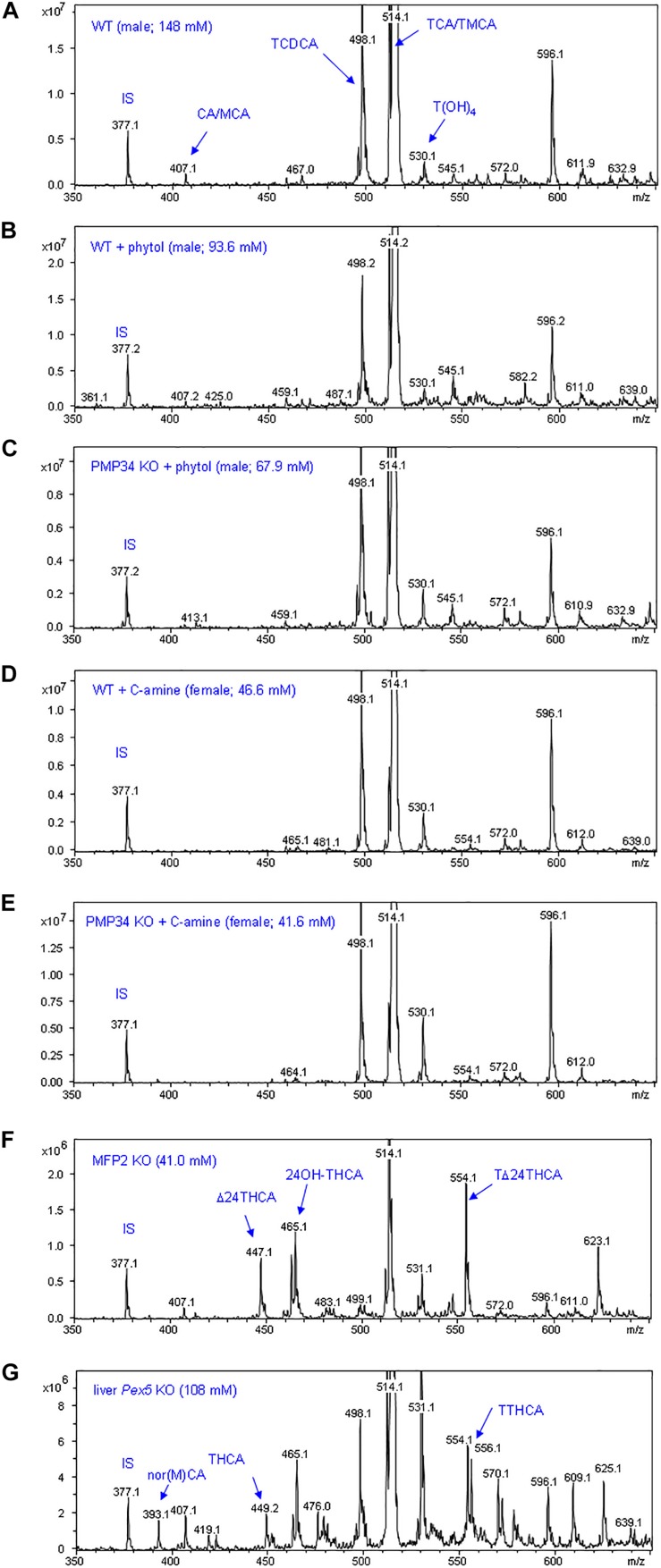
FIGURE 9.
Biliary bile acid profiles of PMP34 KO mice. Panels (A–E) show MS-scans [350-650 m/z; negative mode; smoothed (0.2; 1; GA)] of bile obtained from wild type or PMP34 KO mice fed a normal or a phytol enriched diet or treated with cholesterylamine (C-amine) (gender and concentration of biliary bile acids of the individual animals is indicated in parentheses). Murine bile contains mainly tauro-conjugates, the major ones being tauromuricholic acids (TMCA, a,p-isomers) and taurocholic acid (TCA), both same m/z 514 (signal topped in all panels), followed by taurochenodeoxycholic acid (TCDCA, m/z 498) and a taurotetrahydroxycholanic acid (T(OH)4, m/z 530) (IS, 23-nor-3a,12a-dihydroxy-5p-cholanoic acid, m/z 377). The ion with m/z 596 represents a Na-acetate adduct of m/z 514; non-conjugated bile acids (cholic acid/muricholic acid, CA/MCA, m/z 407; deoxycholic acid, DCA, m/z 393) are hardly visible. In contrast, an abnormal profile is clearly revealed when analyzing bile of a mouse lacking MFP2 (panel F) with accumulation of C27 bile acid intermediates, such as A24-cholestenoic acid (A24-THCA, m/z 447) and its tauroconjugate (TA24THCA, m/z 554), and 24-hydroxycholestanoic acid (24OH-THCA, m/z 465), or a mouse lacking liver peroxisomes (panel G) with abnormal levels of trihydroxycholestanoic acid (THCA, m/z 449) and its tauroconjugate (TTHCA, m/z 556). Nor-CA/MCA (m/z 393), reported in deconjugated bile of SCPx-deficient mice, or their tauroconjugates (m/z 500), were not seen.