Figure 1.
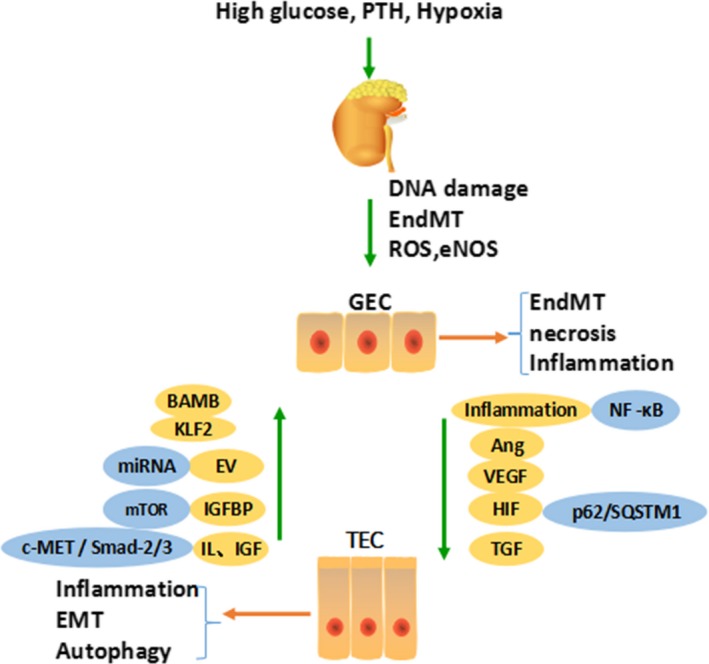
There are many common signalling pathways between TECs and GECs, in which crosstalk plays a vast role. During the occurrence of DKD, abnormal secretion of VEGF, Ang‐1, inflammatory factors and hypoxia promote injury to GECs. Moreover, injured GECs secreting HGF, IGFBPs, EVs, KLF and autophagy can also act on TECs, causing changes in the structure and function of TECs to different degrees. Parathyroid hormone (PTH), glomerular endothelial cell (GEC), tubular epithelial cell (TEC), endothelial‐mesenchymal transition (EndMT), epithelial‐mesenchymal transition (EMT), reactive oxygen species (ROS), endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), angiopoietin (Ang), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), hypoxia‐inducible factor (HIF), tubuloglomerular feedback (TGF), Kruppel‐like factor (KLF), hepatocyte growth factor (HGF/c‐MET), bone activin membrane binding (BAMB), extracellular vesicles (EV), insulin‐like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBPs), insulin‐like growth factor (IGF)
