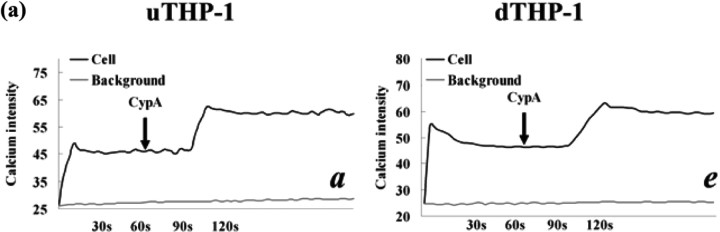
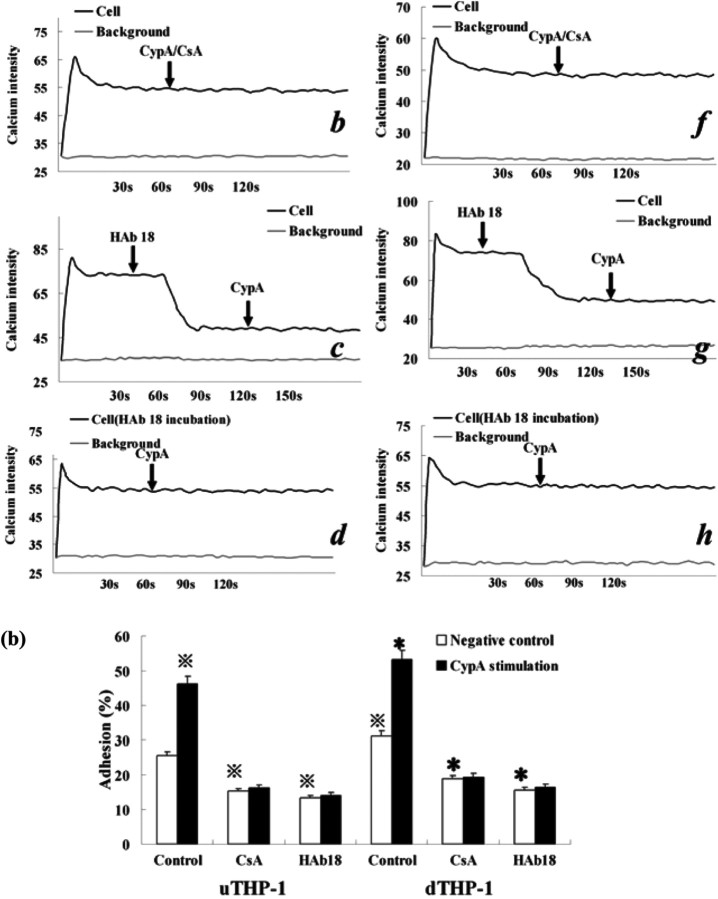
Fig. 8.
CypA-mediated Ca2+ increase and adhesion of the THP-1 cells. (a) Ca2+ mobilization in the Fluo-3-loaded uTHP-1 (a ∼ d) and dTHP-1 (e ∼ h) cells was measured in the presence of CypA (200 ng/ml) (a, e), CypA/CSA (b, f), HAb18 pre-incubation (d, h) or pre-stimulation (c, g). The arrows indicate the addition of the agonist. The calcium intensity that was detected by intensity of green fluorescence correlated well with cytosolic Ca2+ concentration and showed the changing of Ca2+ levels in THP-1 cells. CypA-induced Ca2+ mobilization in both uTHP-1 (a) and dTHP-1 (e) cells while HAb 18 and CSA inhibited CypA-induced Ca2+ mobilization. (b) The uTHP-1 and dTHP-1 cells were pre-treated with HAb18 antibody or CSA and then were stimulated with CypA in Matrigel Matrix-coated 96-well microtitre plates. A significant increase in both uTHP-1 and dTHP-1 cell adhesion was observed with CypA. In contrast, CSA or HAb18 dramatically reduced THP-1 cell adhesion respectively, both in the absence or presence of CypA. Data are expressed as means ± s.d. (n = 3). 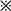 P < 0.05 vs the normal negative uTHP-1 cells. *P < 0.05 vs the normal negative dTHP-1 cells.
P < 0.05 vs the normal negative uTHP-1 cells. *P < 0.05 vs the normal negative dTHP-1 cells.