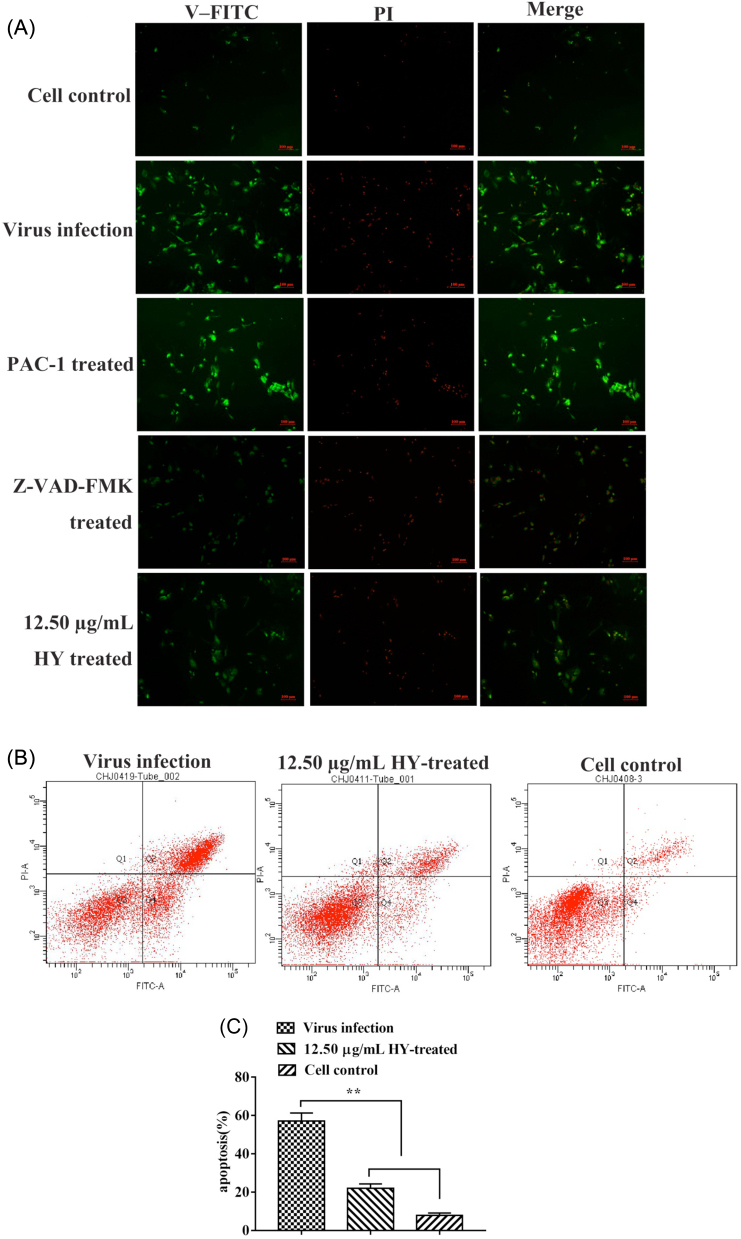
Figure 4.
Effect of the HY on apoptosis in IBV-infected CEK cells. (A) The CEK cells were infected with 100 TCID50 IBV for 1 h at 37˚C followed by incubating 12.5 µg/mL of HY for 30 h. The 20 µM PAC-1-treated CEK cells, 20 µM Z-VAD-FMK pre-treated CEK cells before IBV infection, IBV-infected CEK cells and mock CEK cells were included as control. The green fluorescence signals are designated as the index of early apoptosis in immunofluorescence analysis. Fluorescence intensity (10×) is provided. (B) To quantify the cell apoptosis, the 12.5 µg/mL HY-treated CEK cells after IBV infection, IBV-infected CEK cells and mock CEK cells were stained with Annexin V-FITC and PI, and then analyzed by flow cytometry. Data are presented as dual parameter consisting of Annexin V versus PI. The early apoptosis (Annexin V-FITC staining) and late apoptosis (PI staining) were reflected in Q4 and Q2 gates, respectively. (C) The percentages shown in the column chart are the proportion of apoptotic cells (right panel) in different experimental groups. The differences between means were considered highly significant at **P < 0.01 compared with the IBV-infected control group. CEK = chicken embryo kidney; HY = hypericin; PI = propidium iodide.