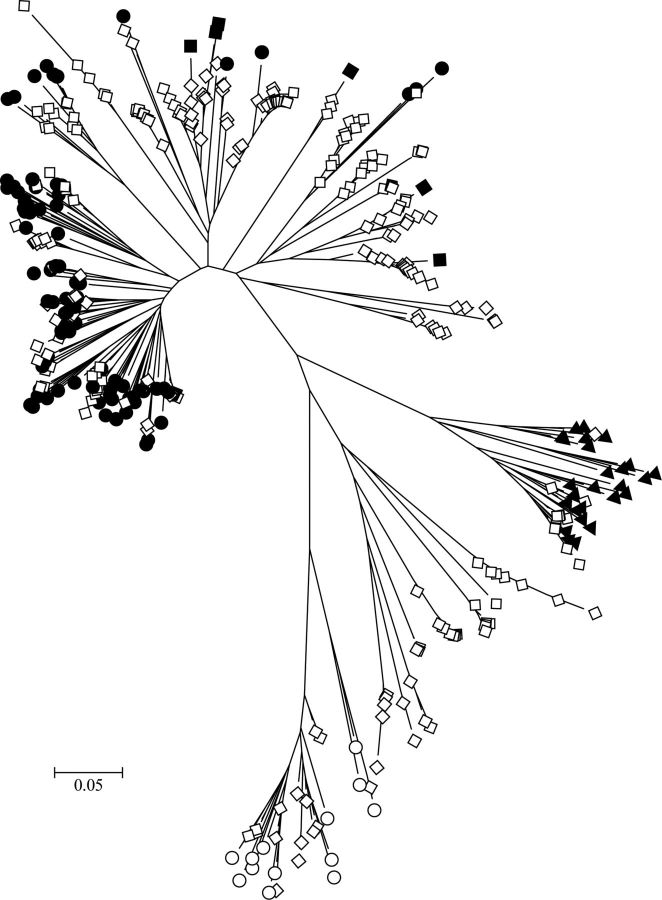
Figure 1.
Evolutionary relationships among characterized and cohort human rhinovirus (HRV) sequences assigned to the genus Enterovirus. The evolutionary history was inferred using the neighbor-joining method in MEGA5 [37, 38]. The optimal tree is shown drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances (base substitutions per site; maximum composite likelihood method [39]) The analysis involved 401 nucleotide sequences, including completely sequenced referenced types [40]. Sequences from this study (open diamonds) were included with previously characterized Human rhinovirus A (filled circles), Human rhinovirus B (filled triangles), Human rhinovirus C (filled diamonds), and enterovirus (open circles) types.