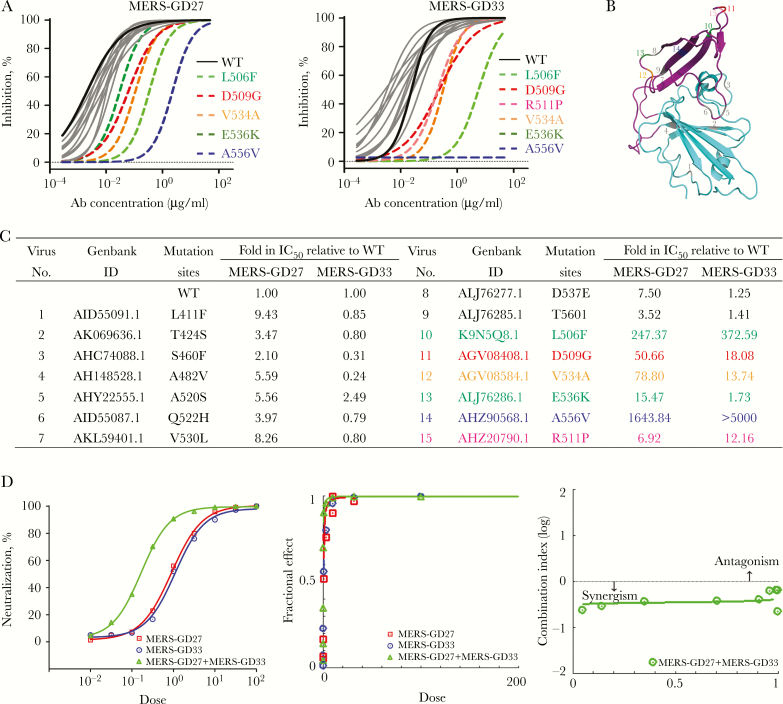
Figure 5.
Epitope mapping by mutagenesis of pseudotyped Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) and combination effects in neutralizing pseudotyped MERS-CoV for MERS-GD27 and MERS-GD33. (A) Neutralizing analysis of MERS-GD27 and MERS-GD33 against MERS-CoV wild-type (WT) and its variant mutants; site-directed mutagenesis was introduced into the WT receptor-binding domain (RBD) sequence to create 15 mutant RBDs of other strains. Discrepant residues significantly reducing the neutralizing activities were indicated by colored and dashed lines, respectively. (B) The spatial relationship of the critical residues. Six highlighted positions and 9 gray positions on the crystal structure of RBD. (C) Summary of inhibition on infection by MERS-GD27 and MERS-GD33 against all pseudotyped viruses bearing the mutant S glycoprotein relative to WT. (D, left) Percentage of neutralization was calculated for serial 3-fold dilutions of each antibody alone and in combination at constant ratios in a range of concentrations from 81 times to 1/81 of half maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC50s). On the x-axis, a dose of 1 was at the IC50 concentration. (Middle) Fractional effect (FA) plots generated by the CompuSyn program. (Right) Median effect plot of calculated combination index (CI) values (logarithmic) versus FA values, in which a log CI of <0 is synergism and a log CI of >0 is antagonism.