Figure 7.
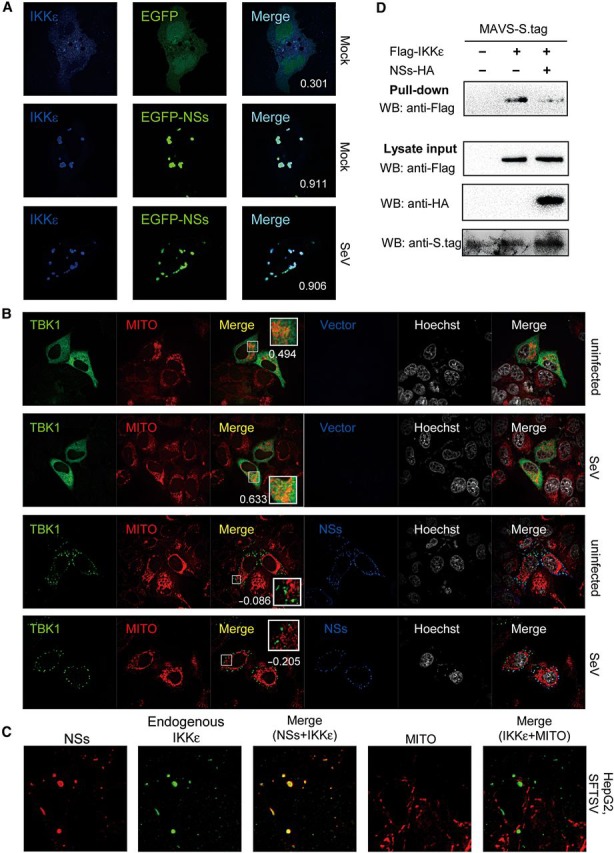
NSs-mediated relocation of TBK1/IKKε leads to irreversible spatial isolation from mitochondria and blocks antiviral signaling. (A) Relocation of kinases to IBs was irreversible upon viral infection. HeLa cells were co-transfected with Flag-IKKε expression plasmids, together with the EGFP or EGFP-NSs expression plasmid. Twenty-four hours later, cells were infected with SeV or left uninfected for 6 h and fixed for IFA. IKKε was stained with anti-Flag. To quantify the co-localization of IKKε and NSs, Pearson's correlation coefficients (PCC) are calculated and shown in the merge column (white numerals). (B) Relocation to IBs leads to irreversible spatial isolation of kinases from mitochondria. Cells were co-transfected with the Flag-TBK1 expression plasmid, and the NSs-S.tag expression plasmid or the empty vector. Twenty-four hours later, cells were infected with SeV or left uninfected for 2 h and stained with mitochondrial marker before being fixed for IFA. TBK1 and NSs were stained with anti-Flag and anti-S.tag, respectively. Nuclei stained with Hoechst are shown in grayscale. To evaluate the localization of TBK1 at mitochondria (MITO), Pearson's correlation coefficients of the signals from green (TBK1) and red (MITO) channels were shown for the representative images (white numerals). See also Supplementary DataA. (C) HepG2 cells were infected with SFTSV for 24 h and stained with mitochondrial marker before IFA. Endogenous IKKε and NSs were revealed with mouse anti-IKKε antibody and rabbit anti-NSs serum, respectively. See also Supplementary DataB. (D) Suppression of IKKε–MAVS association. HEK293 cells were co-transfected with the plasmid encoding MAVS fused with S.tag, along with plasmids expressing IKKε and NSs or their control empty plasmids as indicated. Thirty-six hours post-transfection, cells were treated with SeV for 2 h, and the interaction between IKKε and MAVS was detected by S-protein pull-down assays.
