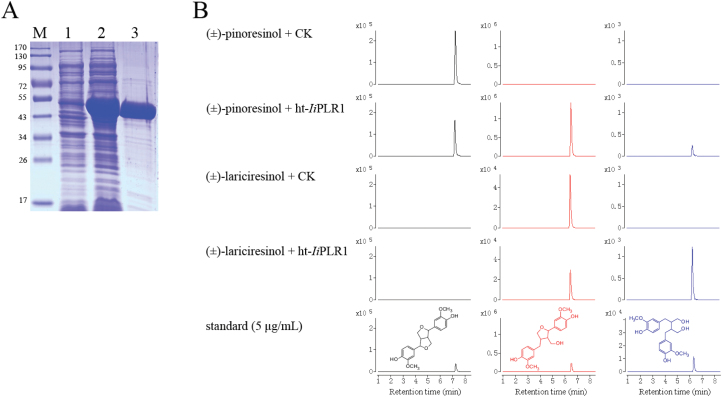
Fig. 6.
Characterization of ht-IiPLR1 produced in E. coli. (A) SDS–PAGE analysis of expression and purification of ht-IiPLR1. Lanes: M, protein marker; 1, uninduced cell harbouring ht-IiPLR1; 2, IPTG-induced cell harbouring ht-IiPLR1; 3, purified ht-IiPLR1. (B) Conversion of (±)-pinoresinol and (±)-lariciresinol by purified ht-IiPLR1. (±)-Pinoresinol (200 μM) and (±)-lariciresinol (3.5 μM) were separately incubated with E. coli cells harbouring the pET32a(+) vector control (CK) and purified ht-IiPLR1 (5 μg ml–1 protein). After 30min of incubation, the reaction products were analysed by LC-MS. (±)-Pinoresinol, (±)-lariciresinol and (±)-secoisolariciresinol were detected by MRM mode with m/z 357→151, 359→329, and 361→164 as the monitoring ion pair, respectively. Chromatograms of (±)-pinoresinol, (±)-lariciresinol, and (±)-secoilariciresinol are denoted with black, red, and blue colour, respectively.