Figure 1.
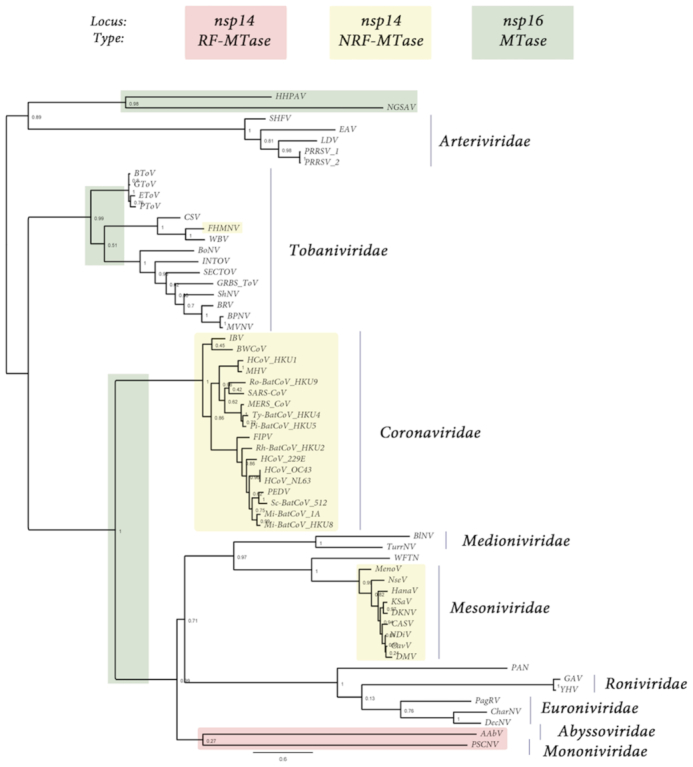
Presence, type and loci of signature-sequences of Nidovirales RNA MTases: RF-MTase of unknown specificity (light red), non-RF « nsp14-like » MT (yellow) and RF « nsp16-like » MTase (green). Both light red and yellow MTases map to the nsp14 C-ter locus, ie. immediately downstrean the ExoN domain, while « nsp16-like » MTase map to the nsp16 locus, at the end of Orf1b. The tree was made based on MAFFT v7.427 multiple sequence alignment with BLOSUM62 scoring matrix and G-INS-i iterative refinement method. The alignments were used as input for maximum likelihood trees generated with the FasTtree v2.1.5 software (best-fit model = JTT-Jones-Taylor-Thorton with single rate of evolution for each site = CAT). Local support values were computed using the Shimodaira-Hasegawa test (SH) with 1000 replicates. Numbers at the nodes represent FasTtree support values and scale var substitutions per site. The tree included two novel Ronivirus-like and Mesonivirus-like genome sequences: Western Flower Thrips Mesonivirus, and Palaemon Nidovirus, respectively (WFTV, PAN, unpublished, see the ‘Materials and Methods’ section and Supplementary Table S1). When present in the NCBI viral genomes database in the 92 Nidovirales complete genomes repository (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/GenomesGroup.cgi?taxid=76804), no accession number is indicated. When an accession number is given in parenthesis, it is referring to the GenBank accession number (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/). The genome dataset used in this study is given in Supplementary Table S1. From top to bottom of the figure: Arteriviridae: HHPAV: Hainan hebius popei arterivirus (MG600021); NGSAV: Nanhai ghost shark arterivirus (MG600024); SHFV: simian hemorrhagic fever virus; EAV: Equine arteritis virus; LDV, Lactate elevating virus; PRRSV-1 and 2, porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Tobaniviridae: BToV: Breda virus; GToV: Goat torovirus; EToV: Berne virus (CAA36747); PToV: Porcine torovirus; CSV: Chinook salmon bafinivirus; FHMNV: Fathead Minnow nidovirus 1; WBV: white bream virus; BoNV: Bovine nidovirus TCH5; INToV: Xinzhou nido-like virus 6; SECToV; Xinzhou toro-like virus 1; GRBS-ToV: Guangdong red banded snake torovirus (MG600030); ShNV: shingleback nidovirus 1 (KX184715); BPNV: Ball python nidovirus 1; MVNV: Morelia viridis nidovirus; BRV: Bellinger River virus (MF685025); Coronaviridae: IBV: Infectious Bronchitis Virus; BWCoV: Beluga Whale coronavirus SW1; HCoV_HKU1: Human coronavirus HK1; MHV: Mouse hepatitis virus; BatCoV_HKU9: Rousettus bat Coronavirus HKU9; SARS-CoV: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus; MERS_CoV: middle-east respiratory syndrome coronavirus; Ty-BatCoV_HKU4: Tylonycteris bat coronavirus HKU4; Pi-BatCoV_HKU5: pipistrellus bat coronavirus HKU5; FIPV: Feline infectious peritonitis virus; Rh-BatCoV-HKU2: Rhinolophus bat coronavirus HKU2; HCoV_229E: Human coronavirus 229E; HCoV_OC43: Human coronavirus OC43 (YP_003766); HCoV_NL63: Human coronavirus NL63; PEDV: Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus; Sc-BatCoV_512: Scotophilus bat coronavirus 512; Mi-BatCoV-1A: bat coronavirus 1A; Mi-BatCoV_HKU8: Miniopterus bat coronavirus HKU8. Medioniviridae: BlNV: Botrylloides leachii nidovirus; TurrNV: Turrinivirus 1; WFTV: Western Flower Thrips virus. Mesoniviridae: MenoV: Meno virus; NseV: Nse virus; HanaV: Hana virus; KSaV: Karang sari virus; DKNV: Dak Nong virus; CASV: Casuarina virus; NDiV: Nam Dinh virus; CavV: Cavally virus; DMV: Dianke mesonivirus. Roniviridae: PAN: Palaemon nidovirus; GAV: Gill-associated virus; YHV: Yellow head virus (EU487200). Euroniviridae: PagRV: Paguronivirus 1; CharNV: Charybnivirus 1; DecNV: Decronivirus 1. Abyssoviridae: AAbV: Aplysia abyssovirus 1. Mononiviridae: PSCNV: Planidovirus 1
