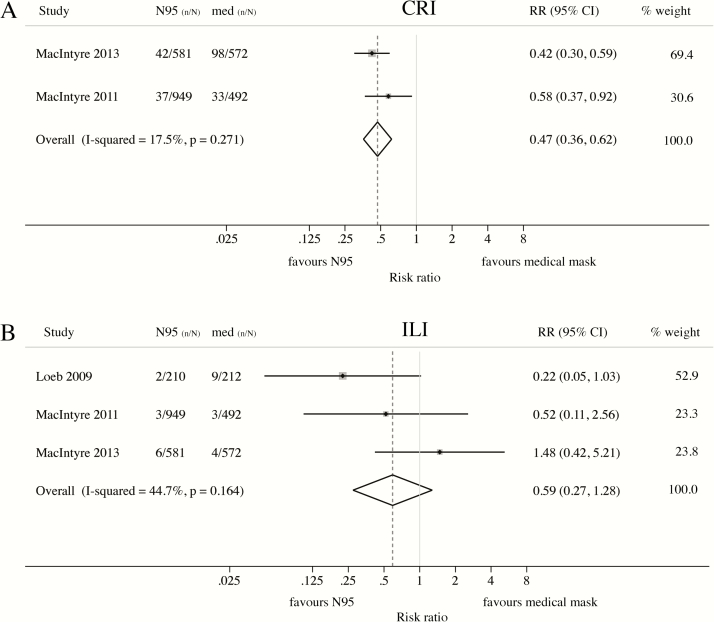
Figure 3.
Meta-analysis of RCTs comparing the protective effect of N95 respirators and medical masks against clinical respiratory outcomes. Protective effect of N95 respirators compared to medical masks against (A) clinical respiratory illness (CRI) or (B) influenza-like illness (ILI). Masks and respirators were worn at all times during the work shift (MacIntyre 2011 [42] and MacIntyre 2013 [44]) or only when providing care to patients with febrile respiratory illness (Loeb 2009 [45]). (A) CRI = 2 or more respiratory symptoms, or 1 respiratory symptom and a systemic symptom; (B) ILI (MacIntyre 2011 [42] and MacIntyre 2013 [44]) = fever ≥38°C and 1 respiratory symptom; ILI (Loeb 2009 [45]) = fever ≥38°C and cough. Abbreviation: CI, confidence interval; n/N, number of cases/number at risk; RCT, randomized controlled trial; RR, risk ratio.