Figure 1.
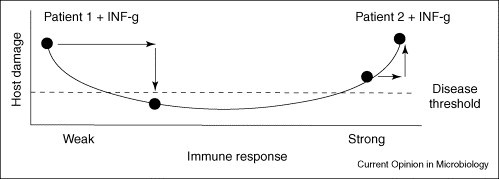
The possible effects of IFN–γ therapy in two patients with cryptococcosis in the context of the Damage-response framework. Patient 1 is an individual with AIDS-related cryptococcosis, where susceptibility to infection is associated with a profound defect in Th1-type immunity as a result of CD4 T-cell deficiency. In this patient, the administration of IFN–γ is pro-inflammatory and the increased inflammatory response might facilitate control of the infection, thus reducing damage and symptoms of disease. By contrast, Patient 2 is an individual with cryptococcal disease following immune reconstitution with HAART. In this patient, administration of IFN–γ might be detrimental, as cryptococcal disease is caused by an exuberant inflammatory response. Hence, the outcome of IFN–γ therapy depends on the immune status of the host.
