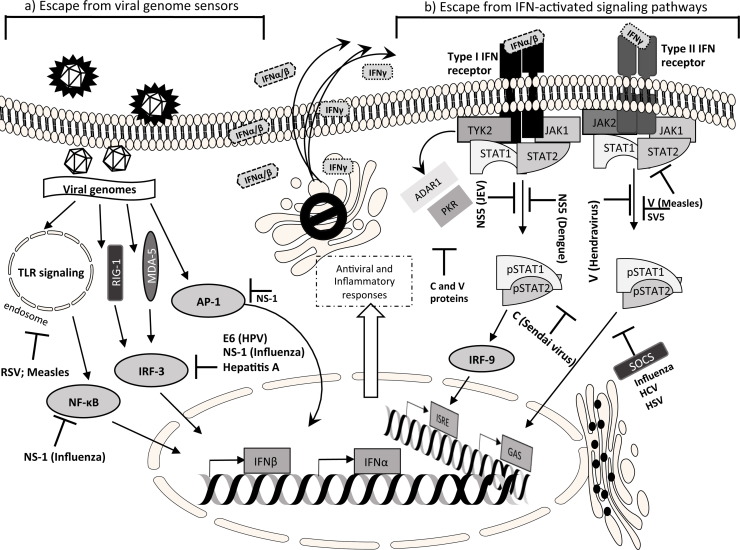
Fig. 1.
A simplified overview of the IFN signaling pathways counteracted by viruses. (a) After the viral entry and uncoating, the detection of viral genome by cytoplasmic or endosomal sensors is prevented by many viral strategies which, on the whole, target the nuclear translocation of transcription factors (NF-κB, IRF-3, AP-1); other strategies include the block of upstream mediators such as MDA-5 or TLRs. (b) Mechanisms that target the IFN cellular response through the block of JAK-STAT signaling pathway: degradation or cytoplasmic sequestration of STAT proteins by reduction of phosphorylation. See text for details. Abbreviations: ADAR1, adenosine deaminase acting on RNA 1; AP-1, activator protein 1; E6 early protein 6 (HPV); GAS, interferonγ-activated sequence; ISRE, interferon stimulated response element; IRF, interferon regulatory factor; JAK, janus kinase; MDA-5, melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5; NF-κB, NF-κB, nuclear factor κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NS-1, non structural protein 1 (Influenza types A, B, C); PKR, protein kinase R; RIG-1, retinoic acid inducible gene 1; RSV, respiratory syncytial virus; SOCS, suppressor of cytokine signaling; STAT, signal transducers and activators of transcription; TYK-2, tyrosine kinase 2, TLR, toll-like receptors.