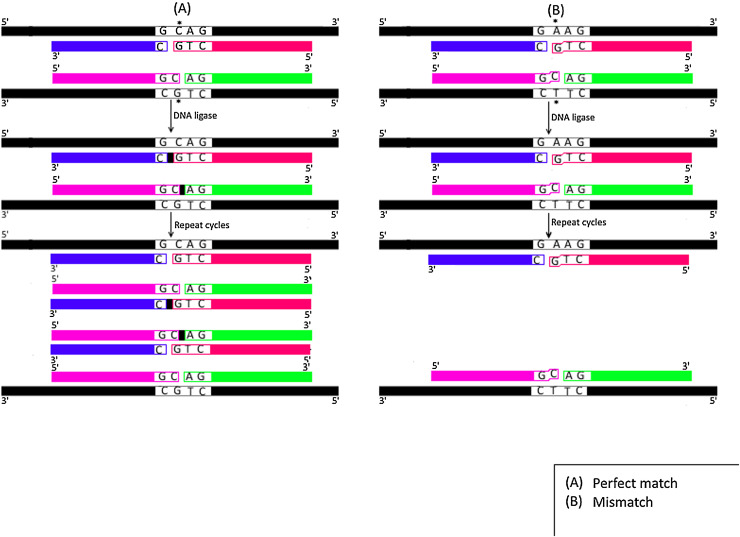
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation for Ligase Chain Reaction (LCR) technique.
A) Perfect Match; Four oligonucleotide primers (each is colored/shaded differently) anneal perfectly with their complementary sequences of perfect match wild type sample (colored in black). DNA ligase enzyme then seal the nick (indicated by small black box) between two adjacent primers hybridizing to the same template strand yielding one ligated fragment for each template strand. Following repeated cycles, exponential ligation of products is achieved. B) Mis-Match; The four oligonucleotide primers (each is colored/shaded differently) do not anneal perfectly with the mis-matched sample that contains only one bp change from wild type sample (colored in black). No ligation is achieved by DNA ligase and hence ligated products are not produced following repeated cycles. Black spot (•) refers to either perfect match (A) or mismatch base (B).