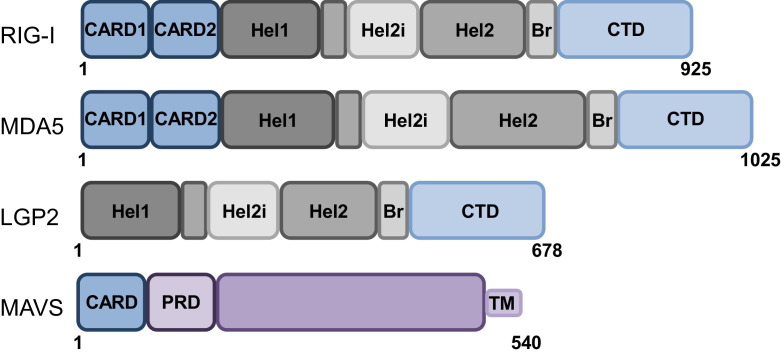
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of RLR and MAVS domain structures. RIG-I and MDA5, but not LGP2, possess tandem caspase activation and recruitment domains (CARDs), a signaling module allowing for MAVS binding and IFN-α/β induction. In addition, all three RLR members have a helicase core consisting of two helicase domains (Hel1 and Hel2), a helicase insertion domain within Hel2 (Hel2i) with ATPase activity, a bridging domain (Br), and a C-terminal domain (CTD). Both the helicase and the CTD have RNA binding abilities. MAVS is comprised of a single CARD, a proline-rich domain (PRD), and a transmembrane (TM) domain that anchors it to mitochondria, peroxisomes, and MAM.