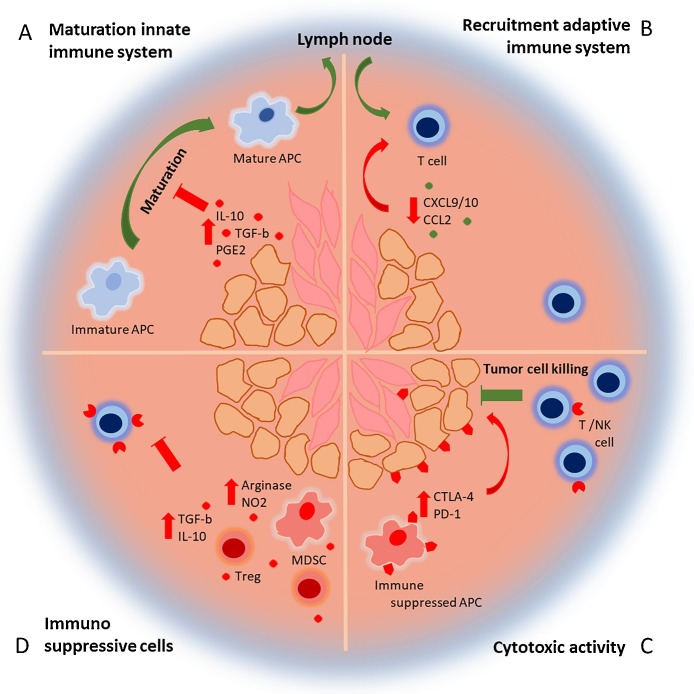
Fig. 1.
The immunosuppressive tumor micro environment. (A) Tumor cells (orange) and stromal cells (pink) secrete immune suppressive molecules, which inhibit the maturation of APCs. Maturated APCs migrate to the lymph node to activate the adaptive immune system. (B) As a result, activated T cells migrate to the tumor driven by a chemokine gradient. However, the secretion of chemokines is lowered in the tumor resulting in reduced T cell infiltration. (C) T cells that enter the TME to target the tumor cells are inhibited by immune suppressive receptors expressed by the tumor, stromal cell, but also immune suppressed APCs. (D) Tregs and MDSCs are recruited to the TME, which secrete more immune suppressive molecules and inhibit the T cell response even further.