Figure 1.
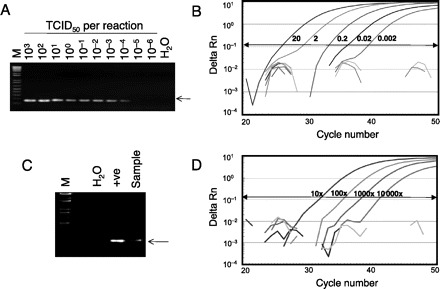
Molecular detection of the novel H1N1 influenza virus by conventional and real-time RT-PCR assays.
(A), Amplification of serially diluted positive control samples. The viral RNA inputs in these reactions are indicated in terms of TCID50. M, 1-kb DNA ladder markers (Invitrogen); H2O, water control; arrow, expected RT-PCR products (173 bp). (B), Amplification of serially diluted positive control samples. The amount of viral RNA (TCID50) used in each of the positive reactions is indicated. (C), Detection of the novel H1N1 from a clinical specimen by the conventional RT-PCR assay. +ve, positive control. (D), Detection of the novel H1N1 from a clinical specimen by the real-time RT-PCR assay. The clinical specimen was serially diluted and tested using the assay. The dilution factors used in each of these positive reactions are indicated. Delta Rn indicates the magnitude of the PCR signal.
